Off the Top: Social Software Entries
Showing posts: 106-120 of 134 total posts
MyWeb 2 Grows Up Quickly into a Usable Tool
Earlier this week I chose to use Yahoo! search rather than the default Google that I usually use. The search page on Yahoo! had sponsored links at the top of the page, but then a few other offerings followed by the usual offerings. The second set was dead on what I was seeking. What were these second set of links? They were the results of those in "My Community" in MyWeb 2 Search, which is similar to del.icio.us in that it is a social bookmarking tool with tagging.
This discovery from a community of less than 40 people really surprised me. Of those 40 people less than 15 have more than 5 pages they have bookmarked, but this community is one I share interests and vocabulary. I was partial shocked with amazement as when MyWeb 2 launched in beta a few weeks ago (or a few months at this point) I was completely under whelmed as most of the links in MyWeb 2 were for things I not only had not interest in, but did not care to have recommended.
As the net effect of more people adding their bookmarks to this socially shared tool grew the value of the tool increased. As it grows I am positive it the aspects of my community will need to get more fine grained so I can say I like the tags from person X (similar to the granular social network which would make better use of the social network for recommender systems that actually could be used and trusted). One of the benefits of MyWeb 2 is that it gets layered on top of Yahoo's search results, which is a great place for this information.
I would love to replicate my del.icio.us bookmarks and tags into MyWeb 2 at Yahoo. The next step would be to feed both systems at the same time from one central interface. There are things in del.icio.us that I really like, but the layering of the social bookmarking and with tagging on top of other tools adds greater value to the user.
Say Hey - If I Knew
I have a deep love of digital technology as an assistive devise and even an enabling device. But, I need something that sits between the digital and the real so to join those worlds.
Here is the problem... I am continually not blanking at who somebody I know in a digital context (through e-mail, a social networking tool (one that works), listserves, blogs, etc.), but their face or just lack of some means of connecting those I know to who they are physically. It continually happens at conferences or when traveling. This happened three times to me at WebVisions with Matt May, Erin Kissane, and Kris Krug. With all three it took some time before it clicked, fortunately with Matt it clicked while I still had time to draw the lines. I would have loved to have chatted with Erin and Kris with the context of how I know them firmly in place. Part of the problem it did not register to me that they were going (I am not sure I checked close enough to the event Upcoming to see who was going to I could make a mental note (or otherwise) to say hey.
What would the solution be? The gap between digital and physical must close. I need my address book crossed with my digital social networks and get all of the pieces tied together with one identity that I can track. Sure everybody can keep their 16 screen names across different communities, but we need to aggregate those to one identity when it makes sense, such as meeting in person. I have been told Sxip can handle this, but I have not had the time to track that down.
The next step is to take the aggregated identity and go through events I am attending or places traveling and let me know who will be there. I am not see this as a privacy issue as there are established friend relationships and set with parameters of securely allowing access to our information, or it has be made public. I usually have a mental list of who I want to see and talk to prior to events, but that group is growing. There is also a group of people I normally only see at events and I always try to hang with that "floating island", but I am usually in contact with them long before.
It seems like a tool like Upcoming would be a perfect place to do this for a large chunk of events. It will still take aggregating the identities across all of the digital communities I belong, address books, and in-person communities. I would love for the next step to include an application in my mobile device that tipped me off to somebody on my friendly "say hey" list being with in "hey" range.
Passion and the Day-to-day
This has been an up and down month so far with health, work, technology, and time. In general 2005 has been a rough year for respiratory issues already for me as I am nearly 3x the normal problems for a full year. These issues zaps energy and fogs the brain (something I really loathe).
The day-job is muddled in past problems, issues that have been plaguing people and have been solved years ago, but where I am resources and bureaucracy keep the long past current. Outside of the day-job I am working with the now and future, which I have really been loving. I have been working on responding back to many questions that have come in through e-mail about possible work and helping people through problems grasping and implementing efficiencies for current web development, folksonomies, and Personal InfoCloud related items.
I have also been working on my presentation for WebVisions, which involves completing it, tearing it apart and nearly starting over. To date I have nearly 25 hours working on this presentation, mostly integrating new material and editing out past content. This is in contrast to day-job presentations, which take me about an hour to build.
In a sense I am still time traveling on my daily commute. The gap is about four to six years of time travel in each 40 minute to hour commute. This is really wearing on me and it is long past time to move on, but I have not had the time to put forward to nail down the essentials for moving my passion to my day job (time and family needs that have filled this year).
So today, I was quite uplifted as my subscription issue of August 2005 MIT Technology Review arrived. The cover topic is Social Machines and I am quoted and have a sidebar box. That was up lifting as it relates to my "real work". This is right up there with Wired's Bruce Sterling article on folksonomy and Thomas Vander Wal.
Now the real work continues. If you are in Portland for Web Visions or just there in general later this week, please drop me a note and I will provide my contact info. If you are not in Portland and would like me to come to you and discuss and help along these topics please contact me also.
Social Machines in MIT Technology Review
In the August issue of MIT Technology Review in Wade Roush's cover story on Social Machines (posted on Wade's site) I get a nice quote. The article is well worth the read, even worth picking up the issue when it hits the stands. The article covers the social, mobile, and continuous computing world that some of us live in and many more will be doing soon. Those of us working at the front of the curve are working on ways to make it smoother for those who will follow along soon.
Convergence and the seamless transfer from stationary computing to continuous computing leads to drastically different interactions with information and media. We are already seeing the shift of people using mobile phones as just a voice communication medium to one that includes text and media interactions, or the from people listening to their mobile phones to looking at their mobile phones. Three years ago I made this shift and I was extremely frustrated as I had many more desires than my mobile phones could assuage. But, it is getting better today even if it takes more human interaction than is really needed to sync information, let alone have moved close to me (or whomever is the wanting to have the information or media stay attracted to themselves or have attracted in certain situations). It is this that is my focus of the Model of Attraction and the focus of the Personal InfoCloud.
Yahoo MyWeb 2.0 Goes Beta
Yahoo has launched Yahoo MyWeb 2.0 today. It has elements of Flickr but not the polish, nor the attention to detail. There are a lot of very rough edges, but there is a lot of potential also. I may spend some time playing around with it in the next few days and weeks. I surely will be sending a ton of feedback in. Hopefully MyWeb will iterate far more rapidly than their blogging software, which had rough edges and they still exist and no noticeable improvements have been made (I don't know many that will recommend it to nubies until the rough edges are fixed).
The tool from the very little I have looked at it seems like it has the broad folksonomy executed well. This seems to have many elements of del.icio.us integrated. I am curious is there is the capability to have community around tags (be same definition).
My curiosity is really piqued with the MyRank search engine. It seems to be a predictive engine of sorts, which really has my interest.
If you want to add me I can be found at tjvanderwal there in Yahoo! type places.
Academic Cites for Interested Parties
One of the things that I am still mulling over that came out of the Social Software in the Academy Workshop is the relationship between academic cites and interested parties (non-academics researching, thinking deeply, and writing about a subject). Over the past year I have had some of the work I have posted on my web sites cited in academic papers. These papers have been for general coursework to graduate thesis.
In the academic realm these cites in other's works give credibility and ranking. In the realm of the professional or "interested party" these cites mean little (other than stroking one's ego). These cites do not translate to higher salary, but they may have some relationship to credibility in a subject area.
Another aspect is finding a way to tie into academic work around these subjects. There are often wonderful academic related gatherings (conferences, symposia, etc.) around these subject matters, but these are foreign to the "interested party". There is a chasm between academic and professional world that should be narrowed or at a minimum bridged in a better way. At SSAW there were some projects I found out about that I would love to follow, or even contribute to in some form (advisement, contributor, etc.).
I have a feeling I will be mulling this for some while, and will be writing about it again.
Post SSAW Snapshot
I had an utterly fantastic weekend at the Social Software in the Academy Workshop at the Annenberg Center for Communication. There were great conversations and shared observations from a broad spectrum of academic interests as well as outside (that was me).
The interview of Richard Cameron of CiteULike covering folksonomies and their value on social bookmarking sites went quite well in my opinion. There was a very robust backchannel (actually two of them, one steno-tracking the panels and the other was free space) that really had some good discussion going in parallel to the interview/conversation.
There are many people I really want to keep in touch with from this weekend as there are some things in the folkonomy and Personal InfoCloud work I am doing as well as general input on where and how to work through the walls between academia and the practitioners (interested and informed parties outside).
I can always tell when I have had a good time interacting with others as I have problems sleeping as I am digesting and culling through conversations and ideas that I have been exposed to. Any even that changes the work I am doing for the better or causes me to pause, reflect, and integrate a new perspective is a fantastic time by me. Although going through this on a 4.5 hour red-eye flight from Long Beach to DC was a little disruptive to normality this morning.
One idea that came up this week end was a workspace that is part academia and part think tank for technology/design ideas to gel and incubate. I had just run across a similar idea in John Thakara's In the Bubble, which he labeled something similar a "think-and-do tank". This sounds like a wonderful environment. Part research and part building to test and improve what is around us seems very well suited to where I am desiring to head. I get lost deep down in the details and most often have to pull my discussions up to a much higher level for others to benefit (not always the case of late, as exposing some of the under belly of the data flow diagrams and technical design elements really would have helped the cause, but I kept getting asked higher level questions and answered there, such is life).
I have been trying to figure out a good home for the Personal InfoCloud (including the related folksonomy and Model of Attraction) as regular work/obsession. I think I am somewhat closer to figuring that out as of this past weekend. I need to get a lot of this out of my head to help others move forward as well. I would love 30 hours days, but that will not happen so I need to deal with the constraints and hand and rework some things to finally get things moving fully in the right direction.
Heading to Los Angeles and SSAW at the Annenberg Center
I am off again this weekend. I will be in Los Angeles this weekend. So far I have most of Friday free. It looks like dinner may be taken on Friday evening as well as a beer or two to acclimate a Brit. Interesting things to see (other than my old house, junior high, and neighborhood) or meet-ups would be quite welcome.
I am at the Social Software in the Academy Workshop at the USC Annenberg Center on Saturday and Sunday. I will be chatting with Richard Cameron of CiteULike on Sunday. Not only does he run CiteULike, but he has been doing some interesting research on trends and patterns, which he is using to improve the probability the person using the service will find what they need more easily. We had a great chat last night and I am really looking forward to the public chat on Sunday.
Presenting at Social Software in the Academy Workshop at the Annenberg Center for Communication
Add to my list of events where I will be presenting, Social Software in the Academy Workshop at the USC Annenberg Center for Communication. This will be May 14-15th. The focus my involvement will be around folksonomy and tagging. I will post more info as the time nears and I know more.
Folksonomy In Wired Magazine
Today was largely an exceptional day. I got a few nice e-mails today that really made my day (more on those some other time). But, today when I got home and settled Andrew popped up on iChat saying he had just opened the April issue of Wired and read the Bruce Sterling article. ["Order Out of Chaos"], about... me. My copy was on the steps and I had not really looked at the mail yet. Andrew pointed me to page 83, to which I had a jaw dropping holy expletive.
I have been getting interviewed a far amount this year and the novelty of seeing one's own name in print has not worn off. But, seeing my own name in Wired magazine, particularly in a Bruce Sterling article, as a little mind numbing. His fact checker had contacted me a few weeks back, but I was not expecting this.
The best thing about the article was Bruce nails folksonomy. But, he not only nails it he provides a couple explanations that stand out:
It was a mob of interested people - folks and the machines working behind the scenes that tossed in some technological onomy. .... Folksonomy emerges from a combination of two inventions: (1) machines that can automate at least some of what it takes to classify information and (b) social software that makes users willing to do at least some of the work for nothing.
It is well worth the read to get a good grasp of where folksonomies work and where they are lacking. Bruce does an excellent job pulling all of the ends together. Now I really wish I could have stayed one more and two more nights at SXSWi just to say hello to Bruce and be prescient enough to thank him in advance.
Explaining and Showing Broad and Narrow Folksonomies
I have been explaining the broad and narrow folksonomy in e-mail and in comments on others sites, as well as in the media (Wired News). There has still been some confusion, which is very understandable as it is a different concept that goes beyond a simple understanding of tagging. I have put together a couple graphics that should help provide a means to make this distinction some what clearer. The folksonomy is a means for people to tag objects (web pages, photos, videos, podcasts, etc., essentially anything that is internet addressable) using their own vocabulary so that it is easy for them to refind that information again. The folksonomy is most often also social so that others that use the same vocabulary will be able to find the object as well. It is important to note that folksonomies work best when the tags used to describe objects are in the common vocabulary and not what a person perceives others will call it (the tool works like no other for personal information management of information on the web, but is also shared with the world to help others find the information).
Broad Folksonomy
Let's begin with the broad folksonomy, as a tool like del.icio.us delivers. The broad folksonomy has many people tagging the same object and every person can tag the object with their own tags in their own vocabulary. This lends itself very easy to applying the power law curve (power curve) and/or net effect to the results of many people tagging. The power terms and the long tail both work.
The broad folksonomy is illustrated as follows. 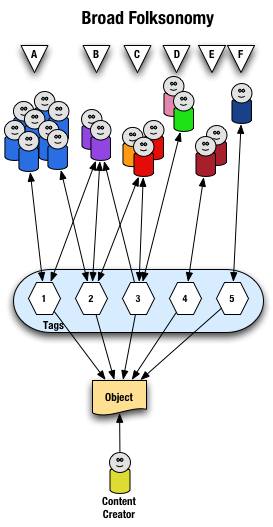
From a high level we see a person creates the object (content) and makes it accessible to others. Other people (groups of people with the same vocabulary represented people blobs and noted with alphabet letters) tag the object (lines with arrows pointing away from the people) with their own terms (represented by numbers). The people also find the information (arrows on lines pointing from the numeric tags back to the people blobs) based on the tags.
Digging a little deeper we see quite a few people (8 people) in group "A" and they have tagged the object with a "1" and a "2" and they use this term to find the object again. Group "B" (2 people) have applied tag "1" and "2" to the object and they use tag terms "1", "2", and "3" to find the information. Group "C" (3 people) have tagged the object with "2" and "3" so that they can find the object. Group "D" has also tagged the object with tag "3" so that they may refind the information this group may have benefitted from the tagging that group "C" provided to help them find the information in the first place. Group "E" (2 people) uses a different term, "4", to tag the object than others before it and uses only this term to find the object. Lastly, group "F" (1 person) uses tag "5" on the object so that they may find it.
Broad Folksonomy and the Power Curve
The broad folksonomy provides a means to see trends in how a broad range are tagging one object. This is an opportunity to see the power law curve at work and show the long-tail.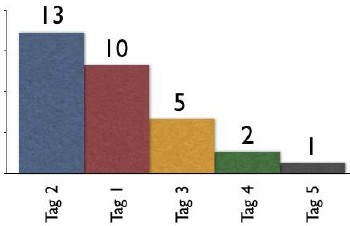
The tags spike with tag "2" getting the largest portion of the tags with 13 entries and tag "1" receiving 10 identical tags. From this point the trends for popular tags are easy to see with the spikes on the left that there are some trends, based on only those that have tagged this object, that could be used extract a controlled vocabulary or at least know what to call the object to have a broad spectrum of people (similar to those that tagged the object, and keep in mind those that tag may not be representative of the whole). We also see those tags out at the right end of the curve, known as the long tail. This is where there is a small minority of people who call the object by a term, but those people tagging this object would allow others with a similar vocabulary mindset to find the object, even if they do not use the terms used by the masses over at the left end of the curve. If we take this example and spread it out over 400 or 1,000 people tagging the same object we will se a similar distribution with even more pronounced spikes and drop-off and a longer tail.
This long tail and power curve are benefits of the broad folksonomy. As we will see the narrow folksonomy does not have the same properties, but it will have benefits. These benefits are non-existent for those just simply tagging items, most often done by the content creator for their own content, as is the means Technorati has done, even with their following tag links to destinations other than Technorati (as they initially had laid out). The benefits of the long tail and power curve come from the richness provided by many people openly tagging the same object.
Narrow Folksonomy
The narrow folksonomy, which a tool like Flickr represents, provides benefit in tagging objects that are not easily searchable or have no other means of using text to describe or find the object. The narrow folksonomy is done by one or a few people providing tags that the person uses to get back to that information. The tags, unlike in the broad folksonomy, are singular in nature (only one tag with the term is used as compared to 13 people in the broad folksonomy using the same tag). Often in the narrow folksonomy the person creating the object is providing one or more of the tags to get things started. The goals and uses of the narrow folksonomy are different than the broad, but still very helpful as more than one person can describe the one object. In the narrow the tags are directly associated with the object. Also with the narrow there is little way of really knowing how the tags are consumed or what portion of the people using the object would call it what, therefore it is not quite as helpful as finding emerging vocabulary or emergent descriptions. We do find that tags used to describe are also used for grouping, which is particularly visible and relevant in Flickr (this is also done in broad folksonomies, but currently not to the degree of visibility that it is done on Flickr, which may be part of the killer interactive environment Ludicorp has created for Flickr).
The narrow folksonomy is illustrated as follows.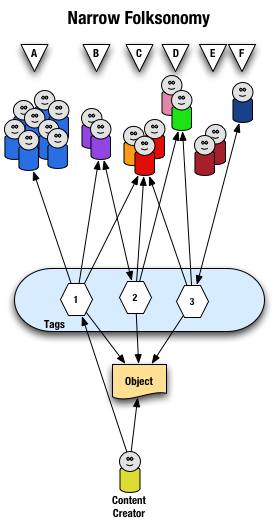
From a high level we see a person creates the object and applies a tag ("1") that represents what they call the object or believe describes the object. There are fewer tags provided than in a broad folksonomy and there is only one of each tag applied to the object. The consumers of the object also can apply tags that help them find the object or describe what they believe are the terms used to describe this object.
A closer look at the interaction between people and the object and tags in a narrow folksonomy shows us that group "A" uses tag "1" to find and come back to the object (did the creator do this on purpose? or did she just tag it with what was helpful to her). We see group "B" also using tag "1" to find the object, but they have tagged the object with tag "2" to also use as a means to find the object. Group "C" uses tag "1","2", and "3" to find the object and we also note this group did not apply any of its own tags to the object as so is only a consumer of the existing folksonomy. We see group "D" uses tags "2" and "3" to find the objects and it too does not add any tags. Group "E" is not able to find the object by using tags as the vocabulary it is using does not match any of the tags currently provided. Lastly, group "F" has their own tag for the object that they alone use to get back to the object. Group "F" did not find the object through existing tags, but may have found the object through other means, like a friend e-mailed them a link or the object was included in a group they subscribe to in their feed aggregator.
We see that the richness of the broad folksonomy is not quite there in a narrow folksonomy, but the folksonomy does add quite a bit of value. The value, as in the case of Flickr, is in text tags being applied to objects that were not findable using search or other text related tools that comprise much of how we find things on the internet today. The narrow folksonomy does provide various audiences the means to add tags in their own vocabulary that will help them and those like them to find the objects at a later time. We are much better off with folksonomies than we were with out them, even if it is a narrow folksonomy being used.
Conclusion
We benefit from folksonomies as the both the personal vocabulary and the social aspects help people to find and retain a tether to objects on the web that are an interest to them. Who is doing the tagging is important to understand and how the tags are consumed is an important factor. This also helps us see that not all tagging is a folksonomy, but is just tagging. Tagging in and of its self is a helpful step up from no tagging, but is no where near as beneficial as opening the tagging to all. Folksonomy tagging can provide connections across cultures and disciplines (an knowledge management consultant can find valuable information from an information architect because one object is tagged by both communities using their own differing terms of practice). Folksonomy tagging also makes up for missing terms in a site's own categorization system/taxonomy. This hopefully has made things a little clearer for all in our understanding the types of folksonomies and tagging and the benefits that can be derived.
This entry first appeared at Personal InfoCloud and comments are open for your use there.
Granular Social Networks to the Rescue
Things have been buzzing around these parts on the folksonomy subject. A few weeks ago I started thinking about social networks (Feedster, Orkut, and LinkedIn) and why they do not work, well other than LinkedIn I do not find much if any useful value. I do think there can be value in social networks and actually believe we will need social networks in the not too distant future.
Why will we need social networks? As personal electronic information publication continues to grow we have more opportunities for shared information that has value for us. The problem will be there will be even more of a deluge of information than there is today when we go seeking information. As people start annotating physical space and tagging physical space we will need the means to quickly parse through the information to find that information that may be the most valuable to us.
Consider standing in front of a restaurant in a city that is new to us. We are considering the menu and look to our mobile phone to see what others have said about the restaurant and there are more than 200 reviews and comments, which is far too many to be read on a mobile phone or even parsed on a mobile phone. But, before we request the reviews and comments our mobile device as noted our location and pushed that out to our predictive services in our Personal InfoCloud (looking at our own reviews, preferences (food and restaurants in this case), and contacts), and checks our social network based on food and restaurant interests. Our phone returns the top 3 reviews and comments that should be of value to us and two of these reviews are three and four degrees from us (could go even farther) in our social network, but based on our food preferences and our trust of our friend s taste in food and restaurants and their service and their friend's same values, and so on. The other review is one who is considered to be the polar opposite of our preferences and can be used to shade our interest.
How did we get to a social network that has needed value? If we take the same folksonomy approach and apply it to social networks we could see social network tools that actually have value. This would work as a narrow folksonomy (like Flickr) with a person tagging people with the connections they trust (or even those they do not trust with a "-" prefix).
The folksonomy is just one option, but social networks have to get far more granular than the broad line that is drawn between people today.
Folksonomy Explanations
The past few weeks have seen my inbox flooded with folksonomy questions. I am going to make things easier on my inbox by posting some common discussions here. Many of the items I am posting I have posted else where, but this will also be a great help for me.
There have been many people who have correctly discerned a difference between the two prime folksonomy examples, Flickr and del.icio.us. As I first stated in a comment to Clay Shirky's first article on Folksonomy, there are two derivations of folksonomy. There is a narrow folksonomy and a broad folksonomy. On August 26th I stated...
Clay, you bring in some very good points, particularly with the semantic differences of the terms film, movie, and cinema, which defy normalization. A broad folksonomy, like del.icio.us, allows for many layers of tagging. These many layers develop patterns of consistency (whether they are right or wrong in a professional's view is another matter, but that is what "the people" are calling things). These patterns eventually develop quasi power law for around the folk understanding of the terms as they relate to items.
Combining the power tags of "skateboarding, tricks, movie " (as you point out) will get to the desired information. The hard work of building a hierarchy is not truly essential, but a good tool that provides ease of use to tie the semantic tags is increasingly essential. This is a nascent example of a semantic web. What is really nice is the ability to use not only the power tags, but also the meta-noise (the tags that are not dominant, but add semantic understanding within a community). In the skateboarding example a meta-noise tag could be gnarly that has resonance in the skate community and adds another layer of refinement for them.
The narrow-folksonomy, where one or few users supply the tags for information, such as Flickr, does not supply power tags as easily. One or few people tagging one relatively narrowly distributed item makes normalizing more difficult to employ an tool that aggregates terms. This situation seems to require a tool up front that prompts the individuals creating the tags to add other, possibly, related tags to enhance the findability of the item. This could be a tool that pops up as the user is entering their tags that asks, "I see you entered mac do you want to add fruit, computer, artist, raincoat, macintosh, apple, friend, designer, hamburger, cosmetics, retail, daddy tag(s)?"
This same distinction is brought up on IAWiki' Folksonomy entry.
Since this time Flickr has added the ability for friends and family (and possibly contacts) to add tags, which gives Flickr a broader folksonomy. But, the focus point is still one object that is being tagged, where as del.icio.us has many people tagging one object. The broad-folksonomy is where much of the social benefit can be derived as synonyms and cross-discipline and cross-cultural vocabularies can be discovered. Flickr has an advantage in providing the individual the means to tag objects, which makes it easier for the object to get found.
This brings to the forefront the questions about Google's Gmail, which allows one person the ability to freely tag their e-mail entries. Is Gmail using a folksonomy? Since Gmail was included in the grouping of on-line tools that were in the discussion of what to call these things (along with Flickr and del.icio.us) when folksonomy was coined I say yes. But, my belief that Gmail uses a folksonomy (regular people's categorization through tagging) relates to it using the same means of one person adding tags so that object can be found by them. This is identical to how people tag in Flickr (as proven by the self-referential "me" that is ever prevalent) and del.icio.us. People tag in their own vocabulary for their own retrieval, but they also will tag for social context as well, such as Flickr's "MacWorld" tags. In this case Wikipedia is a little wrong and needs improving.
I suppose Gmail would be a personal folksonomy to the Flickr narrow folksonomy and the del.icio.us broad folksonomy. There are distinct futures for all three folkonomies to grow. Gmail is just the beginning of personal tagging of digital objects (and physical objects tagged with digital information). Lou Rosenfeld hit the nail on the head when he stated, "I'm not certain that the product of folksonomy development will have much long term value on their own, I'll bet dollars to donuts that the process of introducing a broader public to the act of developing and applying metadata will be incredibly invaluable.". These tools, including Gmail, are training for understanding metadata. People will learn new skills if they have a perceived greater value (this is why millions of people learned Palm's Graffiti as they found a benefit in learning the script).
Everybody has immense trouble finding information in their hierarchal folders on their hard drive. Documents and digital objects have more than one meaning than the one folder/directory, in which they reside. Sure there are short cuts, but tracking down and maintaining shortcuts is insanely awkward. Tags will be the step to the next generation of personal information managment.
Flickr and the Future of the Internet
Peter's post on Flickr Wondering triggers some thoughts that have been gelling for a while, not only about what is good about Flickr, but what is missing on the internet as we try to move forward to mobile use, building for the Personal InfoCloud (allowing the user to better keep information the like attracted to them and find related information), and embracing Ubicomp. What follows is my response to Peter's posting, which I posted here so I could keep better track of it. E-mail feedback is welcome. Enjoy...
You seemed to have hit on the right blend of ideas to bring together. It is Lane's picture component and it is Nadav's integration of play. Flickr is a wonderfully written interactive tool that adds to photo managing and photo sharing in ways that are very easy and seemingly intuitive. The navigations is wonderful (although there are a few tweak that could put it over the top) and the integration of presentational elements (HTML and Flash) is probably the best on the web as they really seem to be the first to understand how to use which tools for what each does best. This leads to an interface that seems quick and responsive and works wonderfully in the hands of many. It does not function perfectly across platforms, yet, but using the open API it is completely possible that it can and will be done in short order. Imagine pulling your favorites or your own gallery onto your mobile device to show to others or just entertain yourself.
Flickr not only has done this phenomenally well, but may have tipped the scales in a couple of areas that are important for the web to move forward. One area is an easy tool to extract a person's vocabulary for what they call things. The other is a social network that makes sense.
First, the easy tool for people to add metadata in their own vocabulary for objects. One of the hinderances of digital environments is the lack of tools to find objects that do not contain words the people seeking them need to make the connection to that object they are desiring. Photos, movies, and audio files have no or limited inherent properties for text searching nor associated metadata. Flickr provides a tool that does this easily, but more importantly shows the importance of the addition of metadata as part of the benefit of the product, which seems to provide incentive to add metadata. Flickr is not the first to go down this path, but it does it in a manner that is light years ahead of nearly all that came before it. The only tools that have come close is HTML and Hyperlinks pointing to these objects, which is not as easy nor intuitive for normal folks as is Flickr. The web moving forward needs to leverage metadata tools that add text addressable means of finding objects.
Second, is the social network. This is a secondary draw to Flickr for many, but it is one that really seems to keep people coming back. It has a high level of attraction for people. Part of this is Flickr actually has a stated reason for being (web-based photo sharing and photo organizing tool), which few of the other social network tools really have (other than Amazon's shared Wish Lists and Linkedin). Flickr has modern life need solved with the ability to store, manage, access, and selectively share ones digital assets (there are many life needs and very few products aim to provide a solution for these life needs or aims to provide such ease of use). The social network component is extremely valuable. I am not sure that Flickr is the best, nor are they the first, but they have made it an easy added value.
Why is social network important? Helping to reduct the coming stench of information that is resultant of the over abundance of information in our digital flow. Sifting through the voluminous seas of bytes needs tools that provide some sorting using predictive methods. Amazon's ratings and that matching to other's similar patterns as well as those we claim as our friends, family, mentors, etc. will be very important in helping tools predict which information gets our initial attention.
As physical space gets annotated with digital layers we will need some means of quickly sorting through the pile of bytes at the location to get a handful that we can skim through. What better tool than one that leverages our social networks. These networks much get much better than they are currently, possibly using broader categories or tags for our personal relationships as well as means of better ranking extended relationships of others as with some people we consider friends we do not have to go far in their group of friends before we run into those who we really do not want to consider relevant in our life structures.
Flickr is showing itself to be a popular tool that has the right elements in place and the right elements done well (or at least well enough) to begin to show the way through the next steps of the web. Flickr is well designed on many levels and hopefully will not only reap the rewards, but also provide inspiration to guide more web-based tools to start getting things right.