Off the Top: Social Software Entries
Showing posts: 46-60 of 134 total posts
Open Conversations and Privacy Needs for Business
I thought I would share the latest press bit around this joint, Thomas Vander Wal was quoted in Inc Magazine What's Next: Shout it Out Loud (or in the August 2007 issue beginning on page 69). The article focuses the need and desire for companies to share and be open with more of their data and information. Quite often companies are getting bit by their privacy around what they do (how their source their products/resources, who they donate money to, etc.) and rumors start. It is far more efficient and helpful to be open with that information, as it gets out anyway.
Ironically, in the same paper issue on page 26 there is a an article about When Scandal Knocks..., which includes a story about Jamba Juice and a blog post that inaccurately claimed it had milk in its products, which could have easily been avoided if Jamba Juice had an ingredients listing on its web site.
The Flip Side
There are two flip sides to this. One is the Apple converse, which is a rare example of a company really making a mythic organization out of its privacy. The second is companies really need privacy for some things, but the control of information is often too extreme and is now more harmful than helpful.
Viable Privacy
I have been working on a much longer post looking at the social software/web tools for and in the enterprise. Much of of the extreme openness touted in the new web charge is not a viable reality inside enterprise. There are a myriad of things that need to be private (or still qualify as valid reasons for many). The list include preparations for mergers and acquisitions, securities information dealings (the laws around this are what drive much of the privacy and are out dated), reorganizations (restructuring and layoffs, which organizations that have been open about this have found innovative solutions from the least likely places), personal employee records, as well as contractual reasons (advising or producing products for competitors in the same industry or market segment). Out side of these issues, which normally add up to under 30 to 40% of the whole of the information that flows through an organization, there is a lot of room for openness in-house and to the outside world.
Need for Enterprise Social Tools Grasping Partial Privacy
When we look at the consumer space for social software there are very few consumer tools that grasp social interaction and information sharing on a granular level (Ma.gnolia, Flickr, and the SixApart tools Vox and LiveJournal are the exceptions that always come to mind). But, many of the tools out there that are commonly used as examples of social web tools really fall down when business looks at them and thinks about privacy and selective sociality (small groups). The social web tools all around really need to grow up and improve in this area. As we are seeing the collaboration and social tools evolve to more viable options we start to see their more glaring holes that do not reflect the reality of human social interaction.
Closing the Gap
What we need is for companies to be more open so the marketplace is a more consumer and communicative environment, but we also need our still early social web tools to reflect our social realities that not everything is public and having tools that better fit those needs.
[Cross-posted at Personal InfoCloud: Open Converastions... with comments open on that posting.]
Sharing and Following/Listening in the Social Web
You may be familiar with my granular social network post and the postings around the Personal InfoCloud posts that get to personal privacy and personal management of information we have seen, along with the Come to Me Web, but there is an element that is still missing and few social web sites actually grasp the concept. This concept is granular in the way that the granular social network is granular, which focusses on moving away from the concept of "broad line friends" that focus on our interest in everything people we "friend", which is not a close approximation of the non-digital world of friend that we are lucky to find friends who have 80 percent common interests. This bit that is missing focusses on the sharing and following (or listening) aspects of our digital relationships. Getting closer to this will help filter information we receive and share to ease the overflow of information and make the services far more valuable to the people using them.
Twitter Shows Understanding
Twitter in its latest modifications is beginning to show that it is grasping what we are doing online is not befriending people or claiming friend, but we are "following" people. This is a nice change, but it is only part of the equation that has a few more variables to it, which I have now been presenting for quite a few years (yes and am finally getting around to writing about). The other variables are the sharing and rough facets of type of information we share. When we start breaking this down we can start understanding the basic foundation for building a social web application that can begin to be functional for our spheres of sociality.
Spheres of Sociality
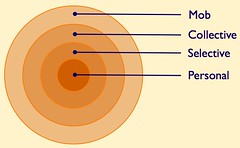 The Spheres of Sociality are broken into four concentric rings:
The Spheres of Sociality are broken into four concentric rings:
- Personal
- Selective
- Collective
- Mob
There are echos of James Surowiecki's Wisdom of Crowds in the Spheres of Sociality as they break down as follows. The personal sphere is information that is just for one's self and it is not shared with others. The selective sphere, which there may be many a person shares with and listens to, are closed groups that people are comfortable sharing and participating with on common interests (family, small work projects, small group of friends or colleagues, etc.). The collective sphere is everybody using that social tool that are members of it, which has some common (precise or vague) understanding of what that service/site is about. The last sphere is the mob, which are those people outside the service and are not participants and who likely do not understand the workings or terminology of the service.
These sphere help us understand how people interact in real life as well as in these social environments. Many of the social web tools have elements of some of these or all of these spheres. Few social web tools provide the ability to have many selective spheres, but this is a need inside most enterprise and corporate sites as there are often small project teams working on things that may or may not come to fruition (this will be a future blog post). Many services allow for just sharing with those you grant to be your followers (like Twitter, Flickr, the old Yahoo! MyWeb 2.0, and Ma.gnolia private groups, etc.). This selective and segmented group of friends needs a little more examination and a little more understanding.
Granular Sharing and Following
 The concepts that are needed to improve upon what has already been set in the Spheres of Sociality revolve around breaking down sharing and following (listening) into more discernible chunks that better reflect our interests. We need to do this because we do not always want to listen everything people we are willing to share with are surfacing. But, the converse is also true we may not want to share or need to share everything with people we want to follow (listen to).
The concepts that are needed to improve upon what has already been set in the Spheres of Sociality revolve around breaking down sharing and following (listening) into more discernible chunks that better reflect our interests. We need to do this because we do not always want to listen everything people we are willing to share with are surfacing. But, the converse is also true we may not want to share or need to share everything with people we want to follow (listen to).
In addition to each relationship needing to have sharing and listening properties, the broad brush painted by sharing and listening also needs to be broken down just a little (it could and should be quite granular should people want to reflect their real interests in their relationships) to some core facets. The core facets should have the ability to share and listen based on location, e.g. a person may only want to share or listen to people when they are in or near their location (keeping in mind people's location often changes, particularly for those that travel or move often). The location facet is likely the most requested tool particularly for those listening when people talk about Twitter and Facebook. Having some granular categories or tags to use as filters for sharing and listening makes sense as well. This can break down to simple elements like work, play, family, travel, etc. as broad categories it could help filter items from the sharing or listening streams and help bring to focus that which is of interest.
Breaking Down Listening and Sharing for Items
| Yourself | Others | |
|---|---|---|
| Share | Yes | Yes/No |
Where this gets us it to an ability to quickly flag the importance of our interactions with others with whom we share information/objects. Some things we can set on an item level, like sharing or just for self, and if sharing with what parameters are we sharing things. We will set the default sharing with ourself on so we have access to everything we do. This follows the Spheres of Sociality with just personal use, sharing with selective groups (which ones), share with the collective group or service, and share outside the service. That starts setting privacy of information that starts accounting for personal and work information and who could see it. Various services have different levels of this, but it is a rare consumer services that has the selective service sorted out (Pownce comes close with the options for granularity, but Flickr has the ease of use and levels of access. For each item we share we should have the ability to control access to that item, to just self or out across the Spheres of Sociality to the mob, if we so wish. Now we can get beyond the item level to presetting people with normative rights.
Listening and Sharing at the Person Level
| Others Settings | ||
|---|---|---|
| Listen/Follow | Yes | No |
| Granular Listen/Follow | Yes | No |
| Granular Share | Yes | No |
| Geo Listen/Follow | Yes | No |
| Geo Share | Yes | No |
We can set people with properties that will help use with default Sphere of Sociality for sharing and listening. The two directions of communication really must be broken out as there are some people we do not mind them listening to the selective information sharing, but we may not have interest in listening to their normal flow of offerings (optimally we should be able to hear their responses when they are commenting on items we share). Conversely, there may be people we want to listen to and we do not want to share with, as we may not know them well enough to share or they may have broken our privacy considerations in the past, hence we do not trust them. For various reasons we need to be able to decide on a person level if we want to share and listen to that person.
Granular Listening and Sharing
Not, only do we have needs and desires for filtering what we share and listen to on the person level, but if we have a means to set some more granular levels of sharing, even at a high level (family, work, personal relation, acquaintance, etc.). If we can set some of these facets for sharing and have them tied to the Spheres we can easily control who and what we share and listen to. Flickr does this quite well with the simple family, friends, contacts, and all buckets, even if people do not use them precisely as such as family and friends are the two selective buckets they offer to work with (most people I know do not uses them precisely as such with those titles, but it provides a means of selective sharing and listening).
Geo Listening and Sharing
Lastly, it is often a request to filter listening and sharing by geography/location access. There are people who travel quite a bit and want to listen and share with people that are currently local or will be local to them in a short period, but their normal conversations are not fully relevant outside that location. Many people want the ability not to listen to a person unless they are local, but when a person who has some relationship becomes local the conversation may want to be shared and/or listened to. These settings can be dependent on the granular listening and sharing parameters, or may be different.
Getting There...
So, now that this is out there it is done? Hmmm, if it were only so easy. The first step is getting developers of social web and social software to begin understanding the social relationships that are less broad lines and more granular and directional. The next step is a social interaction that people need to understand or that the people building the interfaces need to understand, which is if and how to tell people the rights granted are not reciprocal (it is seems to be a common human trait to have angst over non-reciprocal social interactions, but it is the digital realm that makes it more apparent that the flesh world).
Inline Messaging
Many of the social web services (Facebook, Pownce, MySpace, Twitter, etc.) have messaging services so you can communication with your "friends". Most of the services will only ping you on communication channels outside their website (e-mail, SMS/text messaging, feeds (RSS), etc.) and require the person to go back to the website to see the message, with the exception of Twitter which does this properly.
Inline Messaging
Here is where things are horribly broken. The closed services (except Twitter) will let you know you have a message on their service on your choice of communication channel (e-mail, SMS, or RSS), but not all offer all options. When a message arrives for you in the service the service pings you in the communication channel to let you know you have a message. But, rather than give you the message it points you back to the website to the message (Facebook does provide SMS chunked messages, but not e-mail). This means they are sending a message to a platform that works really well for messaging, just to let you know you have a message, but not deliver that message. This adds extra steps for the people using the service, rather than making a simple streamlined service that truly connects people.
Part of this broken interaction is driven by Americans building these services and having desktop-centric and web views and forgetting mobile is not only a viable platform for messaging, but the most widely used platform around the globe. I do not think the iPhone, which have been purchased by the owners and developers of these services, will help as the iPhone is an elite tool, that is not like the messaging experience for the hundreds of millions of mobile users around the globe. Developers not building or considering services for people to use on the devices or application of their choice is rather broken development these days. Google gets it with Google Gears and their mobile efforts as does Yahoo with its Yahoo Mobile services and other cross platform efforts.
Broken Interaction Means More Money?
I understand the reasoning behind the services adding steps and making the experience painful, it is seen as money in their pockets through pushing ads. The web is a relatively means of tracking and delivering ads, which translates into money. But, inflicting unneeded pain on their customers can not be driven by money. Pain on customers will only push them away and leave them with fewer people to look at the ads. I am not advocating giving up advertising, but moving ads into the other channels or building solutions that deliver the messages to people who want the messages and not just notification they have a message.
These services were somewhat annoying, but they have value in the services to keep somebody going back. When Pownce arrived on the scene a month or so ago, it included the broken messaging, but did not include mobile or RSS feeds. Pownce only provides e-mail notifications, but they only point you back to the site. That is about as broken as it gets for a messaging and status service. Pownce is a beautiful interface, with some lightweight sharing options and the ability to build groups, and it has a lightweight desktop applications built on Adobe AIR. The AIR version of Pownce is not robust enough with messaging to be fully useful. Pownce is still relatively early in its development, but they have a lot of fixing of things that are made much harder than they should be for consuming information. They include Microfomats on their pages, where they make sense, but they are missing the step of ease of use for regular people of dropping that content into their related applications (putting a small button on the item with the microformat that converts the content is drastically needed for ease of use). Pownce has some of the checkboxes checked and some good ideas, but the execution of far from there at the moment. They really need to focus on ease of use. If this is done maybe people will comeback and use it.
Good Examples
So who does this well? Twitter has been doing this really well and Jaiku does this really well on Nokia Series60 phones (after the first version Series60). Real cross platform and cross channel communication is the wave of right now for those thinking of developing tools with great adoption. The great adoption is viable as this starts solving technology pain points that real people are experiencing and more will be experiencing in the near future. (Providing a solution to refindability is the technology pain point that del.icio.us solved.) The telecoms really need to be paying attention to this as do the players in all messaging services. From work conversations and attendees to the Personal InfoCloud presentation, they are beginning to get the person wants and needs to be in control of their information across devices and services.
Twitter is a great bridge between web and mobile messaging. It also has some killer features that add to this ease of use and adoption like favorites, friends only, direct messaging, and feeds. Twitter gets messaging more than any other service at the moment. There are things Twitter needs, such as groups (selective messaging) and an easier means of finding friends, or as they are now appropriately calling it, people to follow.
Can we not all catch up to today's messaging needs?
Does IBM Get Folksonomy?
While I do not aim to be snarky, I often come off that way as I tend to critique and provide criticism to hopefully get the bumps in the road of life (mostly digital life) smoothed out. That said...
Please Understand What You Are Saying
I read an article this morning about IBM bringing clients to Second Life, which is rather interesting. There are two statements made by Lee Dierdorff and Jean-Paul Jacob, one is valuble and the other sinks their credibility as I am not sure they grasp what they actually talking about.
The good comment is the "5D" approach, which combines the 2D world of the web and the 3D world of Second Life to get improved search and relevance. This is worth some thinking about, not a whole lot as the solution as it is mentioned can have severe problems scaling. The solution of a virtual world is lacking where it does not augment our understanding much beyond 2D as it leaves out 4 of the 6 senses (it has visual and audio), and provides more noise into a pure conversation than a video chat with out the sensory benefits of video chat. The added value of augmented intelligence via text interaction is of interest.
I am not really sure that Lee Dierdorff actually gets what he is saying as he shows a complete lack of even partial understanding of what folksonomy is. Jacob states, "The Internet knows almost everything, but tells us almost nothing. When you want to find a Redbook, for instance, it can be very hard to do that search. But the only real way to search in 5D is to put a question to others who can ask others and the answer may or may not come back to you. It's part of social search. Getting information from colleagues (online) -- that's folksonomy." Um, no that is not folksonomy and not remotely close. It is something that stands apart and is socially augmented search that can viably use the diverse structures of a folksonomy to find relevant information, but asking people in a digital world for advise is not folksonomy. It has value and it is how many of us have used tools like Twitter and other social software that helps us keep those near in thought close (see Local InfoCloud). There could be a need for a term/word for that Jacob is talking about, but social search seems to be quite relevant as a term.
Related, I do have a really large stack of criticism for the IMB DogEar product that would improve it greatly. It needs a lot of improvement as a social bookmarking and folksonomy tool, but also from the social software interaction side there are things that really must get fixed for privacy interests in the enterprise before it really could be a viable solution. There are much better alternatives for social bookmarking inside an enterprise other than DogEar, which benefits from being part of the IBM social software stack Lotus Connections as the whole stack is decent together, but none of the parts are great, or even better than good by them self. DogEar really needs to get to a much more solid product quickly as their is a lot of interest now for this type of product, but it is only a viable solution if one is only looking at IBM products for solutions.
Understanding Taxonomy and Folksonmy Together
I deeply appreciate Joshua Porter's link to from his Taxonomies and Tags blog post. This is a discussion I have quite regularly as to the relation and it is in my presentations and workshops and much of my tagging (and social web) training, consulting, and advising focusses on getting smart on understanding the value and downfalls of folksonomy tagging (as well as traditional tagging - remember tagging has been around in commercial products since at least the 1980s). The following is my response in the comments to Josh' post...
Response to Taxonomy and Tags
Josh, thanks for the link. If the world of language were only this simple that this worked consistently. The folksonomy is a killer resource, but it lacks structure, which it crucial to disambiguating terms. There are algorithmic ways of getting close to this end, but they are insanely processor intensive (think days or weeks to churn out this structure). Working from a simple flat taxonomy or faceted system structure can be enabled for a folksonomy to adhere to.
This approach can help augment tags to objects, but it is not great at finding objects by tags as Apple would surface thousands of results and they would need to be narrowed greatly to find what one is seeking.
There was an insanely brilliant tool, RawSugar [(now gone thanks to venture capitalists pulling the plug on a one of a kind product that would be killer in the enterprise market)], that married taxonomy and folksonomy to help derive disambiguation (take appleseed as a tag, to you mean Johnny Appleseed, appleseed as it relates to gardening/farming, cooking, or the anime movie. The folksonomy can help decipher this through co-occurrence of terms, but a smart interface and system is needed to do this. Fortunately the type of system that is needed to do this is something we have, it is a taxonomy. Using a taxonomy will save processor time, and human time through creating an efficient structure.
Recently I have been approached by a small number of companies who implemented social bookmarking tools to develop a folksonomy and found the folksonomy was [initially] far more helpful than they had ever imagined and out paced their taxonomy-based tools by leaps and bounds (mostly because they did not have time or resources to implement an exhaustive taxonomy (I have yet to find an organization that has an exhaustive and emergent taxonomy)). The organizations either let their taxonomist go or did not replace them when they left as they seemed to think they did not need them with the folksonomy running. All was well and good for a while, but as the folksonomy grew the ability to find specific items decreased (it still worked fantastically for people refinding information they had personally tagged). These companies asked, "what tools they would need to start clearing this up?" The answer a person who understands information structure for ease of finding, which is often a taxonomist, and a tool that can aid in information structure, which is often a taxonomy tool.
The folksonomy does many things that are difficult and very costly to do in taxonomies. But taxonomies do things that folksonomies are rather poor at doing. Both need each other.
Complexity Increases as Folksonomies Grow
I am continually finding organizations are thinking the social bookmarking tools and folksonomy are going to be simple and a cure all, but it is much more complicated than that. The social bookmarking tools will really sing for a while, but then things need help and most of the tools out there are not to the point of providing that assistance yet. There are whole toolsets missing for monitoring and analyzing the collective folksonomy. There is also a need for a really good disambiguation tool and approach (particularly now that RawSugar is gone as a viable approach).
Company Hallways Loose Great Ideas
One of the panels at the Enterprise 2.0 this week had a panelist mention in the past companies built large campuses so people to be close enough to interact and socialize, but today s tools make that much easier and do not require expensive campuses.
This made me think "company hallways are like the shower, you don t have the means to capture great ideas when they occur".
The Social Enterprise
I am just back from Enterprise 2.0 Conference held in Boston, where I presented Bottom-up All The Way Down: How Tags Help Businesses Organize (thanks to Stowe Boyd for the tantalizing session title), which was liveblog captured by Sandy Kemsley as "Enterprise 2.0: Thomas Vander Wal". I did not catch all of the conference due to some Boston business meetings and connecting with friends and meeting digi-friends whose work I really enjoy face-to-face. The sessions I made it to were good and enlightening and as always the hallway conversations were worth their weight in gold.
Ms. Perceptions and Fear Inside the Corporate Walls
Having not been at true business focussed conference in years (until the past few weeks) I was amazed with how much has changed and how much has stayed the same. I was impressed with the interest and adoption around the social enterprise tools (blogs, wikis, social bookmarking/folksonomy, etc.). But, the misperceptions (Miss Perceptions) are still around and have grown-up (Ms. Perception) and are now being documented by Forrester and others as being fact, but the questions are seemingly not being asked properly. Around the current social web tools (blogs, wikis, social bookmarking, favoriting, shared rating, open (and partially open collaboration) I have been finding little digital divide across the ages. Initially there is a gap when tools get introduced in the corporate environment. But this age gap very quickly disappears if the incredible value of the tools is made clear for people s worklife, information workflow, and collaboration, as well as simple instructions (30 second to 3 minute videos) and simply written clear guidelines that outline acceptable use of these tools.
I have been working with technology and its adoption in corporations since the late 80s. The misperception that older people do not get technology, are foreign to the tools, and they will not ever get the technical tools has not changed. It is true that nearly all newer technologies come into the corporation by those just out of school and have relied on these tools in university to work intelligently to get their degree. But, those whom are older do see the value in the tools once they have exposure and see the value to their worklife (getting their job done), particularly if the tools are relatively simple to use and can be adopted with simple instruction (if it needs a 10 to 200 page manual and more than 15 minutes of training to start using the product effectively adoption will be low). Toby Redshaw of Motorola stated on a panel that he found in Motorola (4600 blogs and wikis and 2600 people using social bookmarking) "people of all ages adopt these tools if they understand the value connected to their work". Personally, I have seen this has always been the case in the last 20 years as this is how we got e-mail, messaging, Blackberries, web pages, word processing, digital collaboration tools (the last few rounds and the current ones), etc. in the doors of small to large organizations. I have worked in and with technically forward organizations and ones that are traditionally thought of as slow adopters and found adoption is based on value to work and ease of use and rarely based on age.
This lack of understanding around value added and (as Toby Redshaw reinforced) "competitive advantage" derived from the social tools available today for use in the enterprise is driven by fear. It is a fear of control that is lost from the top-down. But, the advantage to the company from having this information shared and easy found and used for collaboration to improve knowledge, understanding, and efficiency can not be dismissed and needs to be embraced. The competitive advantage is what is gained today, but next month or next quarter it could mean just staying even.
Getting Beyond Fear
But, what really is important is the communication and social enterprise tools are okay and add value, but the fear is overplayed, as a percentage rarely occurs, and handling the scary stuff it relatively easy to handle.
Tagging and Social Bookmarking in Enterprise
In the halls I had many conversations around tagging ranging from old school tagging being painful because the experts needed to tag things (meaning they were not doing the job as expert they were hired to do and their terms were not widely understood) all the way to the social bookmarking tools are not scaling and able to keep up with the complexity, nor need to disambiguate the terms used. But, I was really impressed with the number of organizations that have deployed some social bookmarking effort (officially or under somebody's desk) and found value (often great value).
Toby Redshaw: I though folksonomy was going to be some Bob Dillon touchy-feely hippy taxonomy thing, but it has off the chart value far and above any thing we had expected.
My presentation had 80 to 90 percent of the people there using social bookmarking tools in some manner in their organization or worklife. The non-verbal feed back as I was presenting showed interest in how to make better sense of what was being tagged, how to use it better in their business, how to integrate with their taxonomy, and how to work with the information as the tools scale. The answers to these are longer than the hour I have, they are more complex because it all depends on the tools, how they are set-up and designed, how they are used, and the structures of information inside and outside their organization.
Stitching Conversation Threads Fractured Across Channels
Communicating is simple. Well it is simple at its core of one person talking with another person face-to-face. When we communicate and add technology into the mix (phone, video-chat, text message, etc.) it becomes more difficult. Technology becomes noise in the pure flow of communication.
Now With More Complexity
But, what we have today is even more complex and difficult as we are often holding conversation across many of these technologies. The communication streams (the back and forth communication between two or more people) are now often not contained in on communication channel (channel is the flavor or medium used to communicate, such as AIM, SMS, Twitter, e-mail, mobile phone, etc.).
We are seeing our communications move across channels, which can be good as this is fluid and keeping with our digital presence. More often than not we are seeing our communication streams fracture across channels. This fracturing becomes really apparent when we are trying to reconstruct our communication stream. I am finding this fracturing and attempting to stitch the stream back together becoming more and more common as for those who are moving into and across many applications and devices with their own messaging systems.
The communication streams fracture as we pick-up an idea or need from Twitter, then direct respond in Twitter that moves it to SMS, the SMS text message is responded back to in regular SMS outside of Twitter, a few volleys back and forth in SMS text, then one person leaves a voicemail, it is responded to in an e-mail, there are two responses back and forth in e-mail, an hour later both people are on Skype and chat there, in Skype chat they decide to meet in person.
Why Do We Want to Stitch the Communication Stream Together?
When they meet there is a little confusion over there being no written overview and guide. Both parties are sure they talked about it, but have different understandings of what was agreed upon. Having the communication fractured across channels makes reconstruction of the conversation problematic today. The conversation needs to be stitched back together using time stamps to reconstruct everything [the misunderstanding revolved around recommendations as one person understands that to mean a written document and the other it does not mean that].
Increasingly the reality of our personal and professional lives is this cross channel communication stream. Some want to limit the problem by keeping to just one channel through the process. While this is well intentioned it does not meet reality of today. Increasingly, the informal networking leads to meaningful conversations, but the conversations drifts across channels and mediums. Pushing a natural flow, as it currently stands, does not seem to be the best solution in the long run.
Why Does Conversation Drift Across Channels?
There are a few reasons conversations drift across channels and mediums. One reason is presence as when two people notice proximity on a channel they will use that channel to communicate. When a person is seen as present, by availability or recently posting a message in the service, it can be a prompt to communicate. Many times when the conversation starts in a presence channel it will move to another channel or medium. This shift can be driven by personal preference or putting the conversation in a medium or channel that is more conducive for the conversation style between people involved. Some people have a preferred medium for all their conversations, such as text messaging (SMS), e-mail, voice on phone, video chat, IM, etc.. While other people have a preferred medium for certain types of conversation, like quick and short questions on SMS, long single responses in e-mail, and extended conversations in IM. Some people prefer to keep their short messages in the channel where they begin, such as conversations that start in Facebook may stay there. While other people do not pay attention to message or conversation length and prefer conversations in one channel over others.
Solving the Fractured Communication Across Channels
Since there are more than a few reasons for the fractured communications to occur it is something that needs resolution. One solution is making all conversations open and use public APIs for the tools to pull the conversations together. This may be the quickest means to get to capturing and stitching the conversation thread back together today. While viable there are many conversations in our lives that we do not want public for one reason or many.
Another solution is to try to keep your conversations in channels that we can capture for our own use (optimally this should be easily sharable with the person we had the conversation with, while still remaining private). This may be where we should be heading in the near future. Tools like Twitter have become a bridge between web and SMS, which allows us to capture SMS conversations in an interface that can be easily pointed to and stitched back together with other parts of a conversation. E-mail is relatively easy to thread, if done in a web interface and/or with some tagging to pull pieces in from across different e-mail addresses. Skype chat also allows for SMS interactions and allows for them to be captured, searched, and pulled back together. IM conversations can easily be saved out and often each item is time stamped for easy stitching. VoIP conversations are often easily recorded (we are asking permission first, right?) and can be transcribed by hand accurately or be transcribed relatively accurately via speech-to-text tools. Voice-mail can now be captured and threaded using speech-to-text services or even is pushed as an attachment into e-mail in services as (and similar to) JConnect.
Who Will Make This Effortless?
There are three types of service that are or should be building this stitching together the fractured communications across channels into one threaded stream. I see tools that are already stitching out public (or partially public) lifestreams into one flow as one player in this pre-emergent market (Facebook, Jaiku, etc.). The other public player would be telecoms (or network provider) companies providing this as a service as they currently are providing some of these services, but as their markets get lost to VoIP, e-mail, on-line community messaging, Second Life, etc., they need to provide a service that keeps them viable (regulation is not a viable solution in the long run). Lastly, for those that do not trust or want their conversation streams in others hands the personally controlled application will become a solutions, it seems that Skype could be on its way to providing this.
Is There Demand Yet?
I am regularly fielding questions along these lines from enterprise as they are trying to deal with these issues for employees who have lost or can not put their hands on vital customer conversations or essential bits of information that can make the difference in delivering what their customers expect from them. Many have been using Cisco networking solutions that have some of these capabilities, but still not providing a catch all. I am getting queries from various telecom companies as they see reflections of where they would like to be providing tools in a Come to Me Web or facilitating bits of the Personal InfoCloud. I am getting requests from many professionals that want this type of solution for their lives. I am also getting queries from many who are considering building these tools, or pieces of them.
Some of us need these solutions now. Nearly all of us will need these solutions in the very near future.
New Profession Unfolding In Beauty and Geekery
A week or more ago I ran across the incredible video of Blaise Aguera y Arcas presentation of Photosynth and Seadragon at TEDTalks 2007. The video is stunning work of Seadragon and Photosynth bringing a collection of images to life from one or more resources.
While the video and ideas behind the tools are incredible displays of where we are today with technology and where we are heading, this caused some ideas I have been trying to get to gel to finally come together. In this video Blaise states (my own transcription):
So what the point here really is, is we can do things with the social environment taking data from everybody, from the entire collective memory of what the earth looks like, and link all of that together and make something emergent that is greater than the sum of the parts. You have a model that emerges of the entire earth, think of it as the long tail to Stephen Lawler s Virtual Earth work. This is something that grows in complexity as people use it and whose benefits become greater to the users as they use it. Their own photos are getting tagged with metadata that somebody else entered. If somebody bothered to tag all of these saints and say who they all are, then my photo of the Notre Dame Cathedral suddenly gets enriched with all of that data. I can use it as an entry point to dive into that space in that metaverse, using everybody else's photos, and do a cross-modal and cross-user social experience that way. Of course a by product of all of that is an immensely rich virtual models of every interesting part of the earth, collected not just from overhead flight and satellite images, but from the collective memory.
Torrent of Human Contributed Digital Content
What this brought together was the incredible amount of human contributed digital content we are sitting on top of at this moment in time. This is not a new concept, but what is different is the skills, tools, and understanding to make use and sense of all this content are having to change incredibly. The Photosynth team is making use of Flickr content that has been annotated by humans (tags, titles, and descriptions), as well as by devices (date, time, location, etc.). This meta information provides hooks put pull disparate information back from its sole beauty and make an even greater beauty and deeper understanding. The collective is better than the pieces, but pulling to collective together in a manner that is coherent, adds value, and brings deeper appreciation is where get hard.
Much of information understanding and sense making to date has relied on human understanding and we have used tools to augment our understanding. But, we now need to rely on deeper analytics in quantitative methods and advanced algorithms to make sense and beauty out of the bits and bytes. The models of understanding are changing to requiring visualizations methods (much like those of Stamen Design) to begin to grasp and see what is happening in our torrent of information at our finger tips and well as make sense of the social interactions of our digitally networked and digitally augmented lives.
Amalgamation of Designer and Quant Geek
What gelled in my mind watching the Blaise demonstration is there is a skill set missing in the next generation comprised of amalgamated design, information use, analytical foundation, and strong quantitative skills. I have clients in start-up businesses and in enterprise that are confronting these floods of information they need to make sense of from folksonomies and customer generated content (including annotations and regular feedback). The skills needed for building taxonomies are not translating well when the volume of information the information managers are dealing with is orders of magnitude higher than what they dealt with previously. The designer, information architect, and taxonomist who have traditionally have dealt with building the systems of information order, access, and use are missing the quantitative skills to analyze and make sense out of a torrent of loosely structured information and digital objects. Those with the quantitative and strong analytical skills have lacked the design and art skills to bring the understanding into frame for regular people grasp and understand.
This class of designer and quant geek is much like the renaissance men, but today the field of those forging new ground is open to men and women. The need to understand not only broad but deep sets of data and information so to contextualize it into understanding is the realm of few, unfortunately as there is a need for many.
I know of limited pockets of people with the skills to do the hard work of querying the vast array of information, objects, and raw data then make something of value of it. But, there needs to be more of these people getting trained as designers with solid quantitative and analytical skills (or the converse). Design shops are missing the quant geeks and engineering shops are missing the visualization geeks that bring this digital world rich in opportunity into something that makes sense and beauty.
If you know people like this that are bored, please let me know as I am finding opportunities flowing.
Full-Day Social Web & Folksonomy Workshop at d.construct
 Tickets for the d.construct Workshops go on sale June 14, 2007. Buying a ticket for a full-day workshop provides free access to the full d.construct conference on September 7th. I am presenting the following workshop on September 6th...
Tickets for the d.construct Workshops go on sale June 14, 2007. Buying a ticket for a full-day workshop provides free access to the full d.construct conference on September 7th. I am presenting the following workshop on September 6th...
Building the Social Web with Tagging / Folksonomies
Thomas Vander Wal, creator of the term folksonomy, provides a full-day workshop on building the social web through a detailed look at tagging systems. The workshop will provide a foundation for understanding social software from the perspective of the people who use it. This perspective helps site owners solve the ‘cold start’ problem of social software not starting out social.
The focus of the workshop is to provide a solid foundation for building and maintaining a social system from the design and management perspective. The workshop will cover policy issues, monitoring, analysis, and tagging systems as features that are added to the mix of existing tools.
The day will provide a brief history of tagging from the days of tagging in the desktop era to current web use. The exercises will focus on better understanding what happens in tagging systems and use those lessons to frame how to build better systems and make better use of the information that is made relevant through those tagging systems. The workshop includes overviews of social web pattern interaction design and the wide array of features.
Folksonomy Book In Progress
Let me start with an announcement. I have not had any answer for continual question after I present on tagging and folksonomy (I also get the question after the Come to Me Web and Personal InfoCloud presentations), which is "where is your book?" Well I finally have an answer, I have signed with O'Reilly to write a book, initially titled Understanding Folksonomy (this may change) and it may also be a wee bit different from your normal O'Reilly book (we will see how it goes).
I am insanely excited to be writing for O'Reilly as I have a large collection of their books from over the years - from the programming PHP, Perl, Python, and Ruby to developer guides on JavaScript, XHTML, XML, & CSS to the Polar Bear book on information architecture, Information Dashboard Design, and Designing Interfaces: Patterns for Effective Interaction Design along with so many more.
Narrowing the Subject
One of the things that took a little more time than I realized it would take is narrowing the book down. I have been keeping a running outline of tagging and folksonomy related subjects that have been in my presentations and workshop as well as questions and answers from these sessions. The outline includes the deep knowledge that has some from client work on the subject (every single client has a different twist and set of constraints. Many of the questions have answers and for some the answers are still being worked out, but the parameters and guidelines are known to get to viable solutions.
Well, when I submitted the outline I was faced with the knowledge that I had submitted a framework for a 800 to 1,000 page book. Huh? I started doing the math based on page size, word counts, bullets in the outline, and projects words per bullet and those with knowledge were right. So, I have narrowed it down to an outline that should be about 300 pages (maybe 250 and maybe a few more than 300).
What Is In This Smaller Book?
I am using my tagging and folksonomy presentations as my base, as those have been iterated and well tested (now presented some version of it well over 50 times). While I have over 300 design patterns captured from tagging service sites (including related elements) only a few will likely be used and walked through. I am including the understanding from a cognitive perspective and the lessening of technology pain that tagging services can provide to people who use them. There will also be a focus on business uses for intranet and web.
When Will This Be Done
Given that I have a rather busy Fall with client work, workshops, and presentations I set a goal to finish the writing by the end of Summer. It sounds nuts and it really feels like grad school all over again, but that is my reality. I have most of the words in my head and have been speaking them. Now I need to write them (in a less dense form than I blog).
Your Questions and Feedback
If you have questions and things you would like covered please e-mail me (contact in the header nav above). I will likely be setting up a blog to share and post questions (this will happen in a couple weeks). I am also looking for sites, organizations, and people that would like to be included in the case studies and interviews (not all will end up in the book, but those that are done will end up tied to the book in some manner). Please submit suggestions for this section if you have any.
Hoping About
Things have been a wee bit busy the past few weeks. I am off to Banff tomorrow (Monday) and boomerang right back after the WWW Conference Tagging Workshop as I have two days of private workshops in DC just following days.
I am off to the 2007 Identity Workshop for a few days, in part to talk to the some TagCommons people face to face, as well as have some client work to follow-up on. I am then off to south of the boarder, for some work before heading back to the office.
Tagging Workshop at d.construct
I should let you know early that I will be doing a full-day tagging workshop prior to d.construct 2007 in Brighton, England in September. I will post more about this as it is announced. The space is rather limited so keep an eye out.
Workshops Near You & Packages
Those interested in the workshop and I will add you to a list for announcing them. If you would like one in your organization or city I can help get this moving. Toward the end of May I will be providing more information about these, the getting smart packages (workshop or presentation combined with days of advising over a set of months). As I have mentioned these to people the interest is quite strong, so if you want more info on these before they are public on the InfoCloud Solutions site drop me an e-mail.
If you have an e-mail that may have an answer that would be longer than 2 minutes to write I likely still have it lined up, but if you want to jump that line, send the e-mail again (or a series of short e-mails with single questions). I am deeply sorry for my delay in responding. I have no excuse, but the need for more time.
From the HQ Office
It has been a good stretch of travel, mostly for work/professional life, but also took a trip to Florida for family holiday. At the moment I am back in the office working on proposals for upcoming projects of various lengths for clients and working through the process of writing, which involves dead trees at the final stages.
Web 2.0 Expo and SF Bay Area
I am soon off again to the San Francisco Bay Area to speak at the O'Reilly Web 2.0 Expo and have business meetings around the Bay Area (please ping via e-mail if you would like to meet-up during this time).
WWW2007 Workshop on Tagging and Metadata
Early next month I am off to Banff to keynote the WWW2007 Workshop on Tagging and Metadata for Social Information Organization. I am not sure how long this trip will be as I will have some pressing work around this time.
Social Software Summit
Lastly, I should note there will be a Social Software Summit that will run at the same time as the ASIS&T IA Summit next Spring (Spring 2008) in Miami. The Social Software Summit is still in its early stages of planning (the idea, dates, location, and interest have been launched). The dates are April 10-11 2008. I have a role in the planning and preparation for this event, along with some other incredible people.
On SXSW Tag You're It Panel
I am a panelist on the Tag You're It Panel at South by SouthWest in Austin, Texas. Others on the panel are the ever fantastic: Heath Row (moderator), George Oates, and Ben Brown. The panel information:
Tag You're It on Saturday 10 March 2007 at 2:00 pm to 3:00 pm. The panel will be looking at what people are actually doing inside social tagging systems and where things have gone in the past couple years with tagging. We will get beyond the notion that tagging is cool by providing examples of how people are really using the tools in innovative and useful ways.
Stop by and say hello.
Analysis of LibraryThing vs. Amazon Tagging Analysis
I have posted my Breaking Down LibraryThing vs. Amazon Tagging Analysis over at Personal InfoCloud. I have spent a lot of time analyzing what Amazon is doing with tagging over the past 16 months. Much of it was missed, but that was not the disappointing bit in the analysis. Most of the comparisons being made were really apples to oranges.
At some point I will write-up an analysis of what Amazon is doing well (some things they are doing brilliantly) and where it has yet to really take advantage of what they have. This will likely have to be broken in to a series as my the two impromptu presentations on the subject have been about an hour long (yes, there is that much there), not including the background set up bits.
I have been including a highlevel view of Amazon tagging in my normally full tagging/folksonomy presentation for the last year or so as there are valuable examples in what is there and their iterations.