Off the Top: Internet Entries
Showing posts: 46-60 of 138 total posts
Designing for the Personal InfoCloud presentation at WebVisions 2005 Wrap-up
I have posted my presentation from yesterday's session at WebVisions, in Portland, Oregon. The files, Designing for the Personal InfoCloud are in PDF format and weigh in at 1.3MB.
I really had a blast at the conference and wish I could have been there the whole day. I will have to say from the perspective of a speaker it is a fantastically run conference. Brad Smith of Hot Pepper Studios did a knock out job pulling this conference together. It should be on the must attend list for web developers. I was impressed with the speakers, the turn out, and how well everything was run. Bravo!
WebVisions is held in one of my favorite cities, Portland, Oregon, which has some of the best architecture and public planning of any North American city. I have more than 300 photos I have taken in 48 hours and will be posting many at Flickr in the next couple of days.
Passion and the Day-to-day
This has been an up and down month so far with health, work, technology, and time. In general 2005 has been a rough year for respiratory issues already for me as I am nearly 3x the normal problems for a full year. These issues zaps energy and fogs the brain (something I really loathe).
The day-job is muddled in past problems, issues that have been plaguing people and have been solved years ago, but where I am resources and bureaucracy keep the long past current. Outside of the day-job I am working with the now and future, which I have really been loving. I have been working on responding back to many questions that have come in through e-mail about possible work and helping people through problems grasping and implementing efficiencies for current web development, folksonomies, and Personal InfoCloud related items.
I have also been working on my presentation for WebVisions, which involves completing it, tearing it apart and nearly starting over. To date I have nearly 25 hours working on this presentation, mostly integrating new material and editing out past content. This is in contrast to day-job presentations, which take me about an hour to build.
In a sense I am still time traveling on my daily commute. The gap is about four to six years of time travel in each 40 minute to hour commute. This is really wearing on me and it is long past time to move on, but I have not had the time to put forward to nail down the essentials for moving my passion to my day job (time and family needs that have filled this year).
So today, I was quite uplifted as my subscription issue of August 2005 MIT Technology Review arrived. The cover topic is Social Machines and I am quoted and have a sidebar box. That was up lifting as it relates to my "real work". This is right up there with Wired's Bruce Sterling article on folksonomy and Thomas Vander Wal.
Now the real work continues. If you are in Portland for Web Visions or just there in general later this week, please drop me a note and I will provide my contact info. If you are not in Portland and would like me to come to you and discuss and help along these topics please contact me also.
Social Machines in MIT Technology Review
In the August issue of MIT Technology Review in Wade Roush's cover story on Social Machines (posted on Wade's site) I get a nice quote. The article is well worth the read, even worth picking up the issue when it hits the stands. The article covers the social, mobile, and continuous computing world that some of us live in and many more will be doing soon. Those of us working at the front of the curve are working on ways to make it smoother for those who will follow along soon.
Convergence and the seamless transfer from stationary computing to continuous computing leads to drastically different interactions with information and media. We are already seeing the shift of people using mobile phones as just a voice communication medium to one that includes text and media interactions, or the from people listening to their mobile phones to looking at their mobile phones. Three years ago I made this shift and I was extremely frustrated as I had many more desires than my mobile phones could assuage. But, it is getting better today even if it takes more human interaction than is really needed to sync information, let alone have moved close to me (or whomever is the wanting to have the information or media stay attracted to themselves or have attracted in certain situations). It is this that is my focus of the Model of Attraction and the focus of the Personal InfoCloud.
On the Apple Front: Watching was Enjoyable
Last night I watched the Steve Jobs keynote to the 2005 WWDC where he announced the move to Intel based processors. While I still have questions (do we get 64bit computing on Intel anytime soon and will we get dual processing anytime soon (soon is relative as the transition is more than a year away and the PowerMacs will not be transitioned until 2008) I was very impressed with the OS development and code compiling tools Apple has put together to run applications on both processors. This seems to solve the Osborne computer paradox of announcing a new product too far out and the demand for the current product dries up (I should not the Osborne Executive was my first personal computer it was considered a portable).
But, the thing I was most impressed with last evening was the video itself. It was running on Quicktime 7 and the viewing window was larger than streamcasts in the past and the quality was extremely good. I was actually very impressed with the quality. I have thought the quality of Quicktime movies is the best of any digital video platform for the web, but this just knocked all others out of the water. Not only was it a wonderful picture, but it seemed to use half of the bandwidth of previous streamcasts.
Tall Stories of Architecture
Those of you interested in architecture the BBC's In Business has a MP3 (podcast if you want) for down load of its program, "Tall Stories". The download will be replaced on Thursday June 2nd so go grab it now.
The half hour radio segment looks at the current state of architecture, architects, and public design in general (largely in Britain, but it includes world examples and is relevant to just about anywhere. There are some good analogies and frameworks for anybody in the design professions.
Wade Roush and 10,000 Brianiacs
I have been following Wade Roush' continuousblog since its inception a few weeks ago. Continuousblog is focussing on the convergence that is finally taking place in the information technology realm. I had a wonderful conversation with Wade last week and have been enjoying watching his 10,000 Brainiacs evolve in 10,000 Brianiacs, Part 1; 10,000 Brainiacs, Part 2; 10,000 Brainiacs, Part 3; and soon to be 10,000 Brianiacs, Part 4.
Wade's concept of "continuous computing" fits quite nicely in line with the Personal InfoCloud as we have access to many different devices throughout our lives (various operating systems, desktops, laptops, PDA, mobile phone, television/dvr, as well as nearly continuous connectivity, etc.). The Personal InfoCloud focusses on designing and developing with the focus on the person and their use of the information as well as the reuse of the information. It is good to see we have one more in the camp that actually sees the future as what is happening to day and sending the wake-up call out that we need to be addressing this now as it is only going become more prevalent.
Opening Old Zips and Finding Missing Passion
Tonight I finally got my old USB Zip drive to work with my laptop (I have not tried in a couple years) and it worked like a charm. I decided to pull most of the contents of my old Zips into my hard drive, as it is backed-up.
I started opening old documents from a project from four and five years ago and the documentation is so much better and detailed that what I have these days. The difference? Focus and resources. On that project I was researching, defining, iterating, and testing one project full-time. I was working with some fantastic developers that were building their parts and a designer that could pulled everything together visually. We each had our areas of expertise and were allowed to do what we enjoyed and excelled at to the fullest. Our passions could just flow. The project was torn apart by budgets and politics with the real meat of it never going live. A small piece of it went live, but nothing like we had up and running. But, this is the story of so many killer projects and such is life.
What is different between now and then? Today there is no focus and no resources to develop and design. I am in an environment overseeing 2,000 projects a year across 15 funding areas (most of the work done centrally is done on 5 funding areas), it is project traffic management, not design, not research design, not iterating, just balancing high priority projects (mostly it is 9 of us cleaning up others poor work). The team I work with is fantastic, but we have few resources (mostly time is missing) to do incredible work.
The looking back at the volumes of documents I wrote laying out steps, outlines of design elements, content assessments, schematics, data flows, wireframes, and Flash animations demonstrating how the finished tools would function I realize I miss that, deeply. I miss the passion and drive to make something great. I miss being permitted to dream big and solve problems that were untouchable, and best of all, go execute on those dreams. When I see members that made up that old team we reminisce, much like guys do about high school sports champion teams they were on. We had a great team with each of us doing what we loved and changing our part of the world, the digital world.
It was in that project that the seeds were planted for everything I love working on now. Looking at old diagrams I see hints of the Model of Attraction. I was using scenarios around people using and reusing information, which became the Personal InfoCloud. These elements were used to let others in on our dreams for that project and it was not until my time on the project was winding down (or there was no desire to move more of the whole product live and therefore no need for my skills) that I could pull out what worked well on project that made it special. Now others are getting to understand the Personal InfoCloud and other frameworks and models I have been sharing.
State is the Web
The use and apparent mis-use of state on the web has bugged me for some time, but now that AJAX, or whatever one wants to call "XMLHttpRequests", is opening the door to non-Flash developers to ignore state. The latest Adaptive Path essay, It's A Whole New Internet, quotes Michael Buffington, "The idea of the webpage itself is nearing its useful end. With the way Ajax allows you to build nearly stateless applications that happen to be web accessible, everything changes." And states, "Where will our bookmarks go when the idea of the 'webpage' becomes obsolete?"
I agree with much of the article, but these statements are wholly naive in my perspective. Not are they naive, but they hold up examples of the web going in the wrong direction. Yes, the web has the ability to build application that are more seemless thanks to the that vast majority of people using web browsers that can support these dynamic HTML techniques (the techniques are nothing new, in fact on intranets many of us were employing them four or five years ago in single browser environments).
That is not the web for many, as the web has been moving toward adding more granular information chunks that can be served up and are addressible. RESTful interfaces and "share this page" links are solutions. The better developers in the Flash community has been working to build state into their Flash presentations to people can link to information that is important, rather than instructing others to click through a series of buttons or wait through a few movies to get to desired/needed information. The day of one stateless interface for all information was behind us, I hope to hell it is not enticing a whole new generation of web developers to lack understanding of state.
Who are providing best examples? Flickr and Google Maps are two that jump to mind. Flickr does one of the best jobs with fluid interfaces, while keeping links to state that is important (the object that the information surrounds, in this case a photograph). Google Maps are stunning in their fluidity, but during the whole of one's zooming and scrolling to new locations the URL remains the same. Google Map's solution is to provide a "Link to this page" hyperlink (in my opinion needs to be brought to the visual forefront a little better as I have problems getting people to recognize the link when they have sent me a link to maps.google.com rather than their intended page).
Current examples of a poor grasp of state is found on the DUX 2005 conference site. Every page has the same URL, from the home page, to submission page, to about page. You can not bookmark the information that is important to yourself, nor can you send a link to the page your friend is having problems locating. The site is stateless in all of its failing glory. The designer is most likely not clueless, just thoughtless. They have left out the person using the site (not users, as I am sure their friends whom looked at the design thought it was cool and brilliant). We have to design with people using and resusing our site's information in mind. This requires state.
When is State Helpful?
If you have important information that the people using your site may want to directly link to, state is important as these people will need a URL. If you have large datasets that change over time and you have people using the data for research and reports, the data must have state (in this case it is the state of the data at some point in time). Data that change that does not have state will only be use for people that enjoy being selected as a fool. Results over time will change and all good academic research or professional researchers note the state of the data with time and date. All recommendations made on the data are only wholly relevant to that state of the data.
Nearly all blogging tools have "permalinks", or links that link directly to an unchanging URL for distinct articles or postings, built into the default settings. These permalinks are the state function, as the main page of a blog is fluid and ever changing. The individual posts are the usual granular elements that have value to those linking to them (some sites provide links down to the paragraph level, which is even more helpful for holding a conversation with one's readers).
State is important for distinct chunks of information found on a site. Actions do not seem state-worthy for things like uploading files, "loading screens", select your location screens (the pages prior and following should have state relative to the locations being shown on those pages), etc.
The back button should be a guide to state. If the back button takes the user to the same page they left, that page should be addressable. If the back button does not provide the same information, it most likely should present the same information if the person using the site is clicking on "next" or "previous". When filling out an application one should be able to save the state of the application progress and get a means to come back to that state of progress, as people are often extremely aggravated when filling out longs forms and have to get information that is not in reach, only to find the application times out while they are gone and they have to start at step one after being many steps into the process.
State requires a lot of thought and consideration. If we are going to build the web for amateurization or personal information architectures that ease how people build and structure their use of the web, we must provide state.
Tech Expo Fose was Ho Hum
I made it to Fose (the government-centric tech trade show) today. I was impressed nor intrigued by extremely little. There was mobile and a very good showing from the Open Source community, old old news to non-government folks. I was completely blown away by many booth's lack of understanding of their own products, particularly the Microsoft booth, I was interested in the One Note as it seemed similar to Entourage's Project (they were unfamiliar with any of the Microsoft Mac products and did not know they made products for the Mac - although they did laugh at my Keynote is PowerPoint with out swearing quip). The MS booth was pushing the product, but nobody seemed to have a clue about it. I was also interested in Groove (I was a fan from when I was using the beta of it many years ago) and wanted to see its current state. Microsoft really needs to hire people who not only care about their products but know about their products and what the company is doing. (This is truly not a Microsoft slam as I am getting some long long lost respect for them on some small fronts.)
I was quite impressed with three booths, Apple, Adobe, and Fig Leaf Software as they were extremely knowledgeable and were showcasing their wares and skills and not goofy side-shows. They had the skills and wares to show off (Blackberry also had a good booth, but I did not have a great interest there).
Apple was showcasing their professional line of hardware, including their servers and SAN, which blew all other server solutions out of the water on price and capability (including Dell and HP). Apple was also showcasing their new OS Tiger, which they were able to show me does search, using Spotlight, in the files comments in the metadata (now labeled Spotlight comments just to make it clear), which will make my life so much wonderfully better, but that is an other post all together. Tiger's Dashboard was also very impressive as it has an Expose-like fade-in ability. I tried asking the same questions to a few different people at the Apple booth and they were all extremely knowledgeable and across the board may have been the most impressive for this.
I hounded Adobe about their InDesign CS2, GoLive CS2 (standards compliance), and Acrobat (tag creation and editing). Not every person could answer every question, but they were able to bring over the right person who had deep knowledge of the product. Adobe has products I like, but there has always been one or two tripping points for me that keep me from fully loving their products and from using their products exclusively in Web development workflow.
The guy at the Fig Leaf booth (a Macromedia training and development shop in Washington, DC. I asked why no Macromedia and was told they pulled out at the last minute, but I had to thank the folks at Fig Leaf as they have the best Macromedia training anywhere in the area (nobody else comes remotely close and most others are a complete waste of time and money). I was really looking for Macromedia to talk about ColdFusion as their last product was so poorly supported by Macromedia it has been strongly considered to drop the product from the workflow. Fig Leaf, not Macromedia was the firm that posted the work arounds to ColdFusion server flaws when you run the CF MX product in a secure Microsoft environment. There is a lot about the Macromedia site that is really difficult to use and it is nearly impossible to find the information you want as well as get back to that same information. Macromedia does make some very good products and they have been very receptive to web standards for quite some time, but there are things that make embracing them so very difficult.
Overall, I got a lot from the show, if only from a very small number of vendors. I think I am finally going to switch up to the Adobe CS2 Premium Suite as it seems like a very good suite, and it has been difficult getting the cross-platform upgrade for the Windows to Mac switch from my PhotoShop 6 license (thanks to help from people in the booth that may be less painful than the two or three hour calls I have previously endured). Also thanks to the faux doctor who handed me a bottle of mint candy pills from the Blackberry booth (chili dog with onions was not good fair prior to going to Fose).
Explaining and Showing Broad and Narrow Folksonomies
I have been explaining the broad and narrow folksonomy in e-mail and in comments on others sites, as well as in the media (Wired News). There has still been some confusion, which is very understandable as it is a different concept that goes beyond a simple understanding of tagging. I have put together a couple graphics that should help provide a means to make this distinction some what clearer. The folksonomy is a means for people to tag objects (web pages, photos, videos, podcasts, etc., essentially anything that is internet addressable) using their own vocabulary so that it is easy for them to refind that information again. The folksonomy is most often also social so that others that use the same vocabulary will be able to find the object as well. It is important to note that folksonomies work best when the tags used to describe objects are in the common vocabulary and not what a person perceives others will call it (the tool works like no other for personal information management of information on the web, but is also shared with the world to help others find the information).
Broad Folksonomy
Let's begin with the broad folksonomy, as a tool like del.icio.us delivers. The broad folksonomy has many people tagging the same object and every person can tag the object with their own tags in their own vocabulary. This lends itself very easy to applying the power law curve (power curve) and/or net effect to the results of many people tagging. The power terms and the long tail both work.
The broad folksonomy is illustrated as follows. 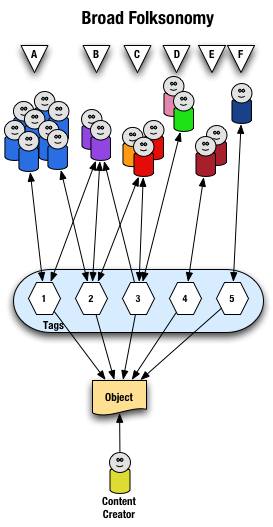
From a high level we see a person creates the object (content) and makes it accessible to others. Other people (groups of people with the same vocabulary represented people blobs and noted with alphabet letters) tag the object (lines with arrows pointing away from the people) with their own terms (represented by numbers). The people also find the information (arrows on lines pointing from the numeric tags back to the people blobs) based on the tags.
Digging a little deeper we see quite a few people (8 people) in group "A" and they have tagged the object with a "1" and a "2" and they use this term to find the object again. Group "B" (2 people) have applied tag "1" and "2" to the object and they use tag terms "1", "2", and "3" to find the information. Group "C" (3 people) have tagged the object with "2" and "3" so that they can find the object. Group "D" has also tagged the object with tag "3" so that they may refind the information this group may have benefitted from the tagging that group "C" provided to help them find the information in the first place. Group "E" (2 people) uses a different term, "4", to tag the object than others before it and uses only this term to find the object. Lastly, group "F" (1 person) uses tag "5" on the object so that they may find it.
Broad Folksonomy and the Power Curve
The broad folksonomy provides a means to see trends in how a broad range are tagging one object. This is an opportunity to see the power law curve at work and show the long-tail.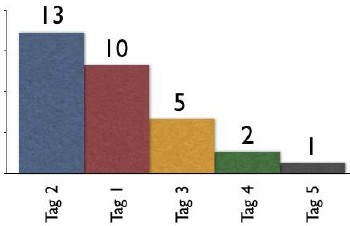
The tags spike with tag "2" getting the largest portion of the tags with 13 entries and tag "1" receiving 10 identical tags. From this point the trends for popular tags are easy to see with the spikes on the left that there are some trends, based on only those that have tagged this object, that could be used extract a controlled vocabulary or at least know what to call the object to have a broad spectrum of people (similar to those that tagged the object, and keep in mind those that tag may not be representative of the whole). We also see those tags out at the right end of the curve, known as the long tail. This is where there is a small minority of people who call the object by a term, but those people tagging this object would allow others with a similar vocabulary mindset to find the object, even if they do not use the terms used by the masses over at the left end of the curve. If we take this example and spread it out over 400 or 1,000 people tagging the same object we will se a similar distribution with even more pronounced spikes and drop-off and a longer tail.
This long tail and power curve are benefits of the broad folksonomy. As we will see the narrow folksonomy does not have the same properties, but it will have benefits. These benefits are non-existent for those just simply tagging items, most often done by the content creator for their own content, as is the means Technorati has done, even with their following tag links to destinations other than Technorati (as they initially had laid out). The benefits of the long tail and power curve come from the richness provided by many people openly tagging the same object.
Narrow Folksonomy
The narrow folksonomy, which a tool like Flickr represents, provides benefit in tagging objects that are not easily searchable or have no other means of using text to describe or find the object. The narrow folksonomy is done by one or a few people providing tags that the person uses to get back to that information. The tags, unlike in the broad folksonomy, are singular in nature (only one tag with the term is used as compared to 13 people in the broad folksonomy using the same tag). Often in the narrow folksonomy the person creating the object is providing one or more of the tags to get things started. The goals and uses of the narrow folksonomy are different than the broad, but still very helpful as more than one person can describe the one object. In the narrow the tags are directly associated with the object. Also with the narrow there is little way of really knowing how the tags are consumed or what portion of the people using the object would call it what, therefore it is not quite as helpful as finding emerging vocabulary or emergent descriptions. We do find that tags used to describe are also used for grouping, which is particularly visible and relevant in Flickr (this is also done in broad folksonomies, but currently not to the degree of visibility that it is done on Flickr, which may be part of the killer interactive environment Ludicorp has created for Flickr).
The narrow folksonomy is illustrated as follows.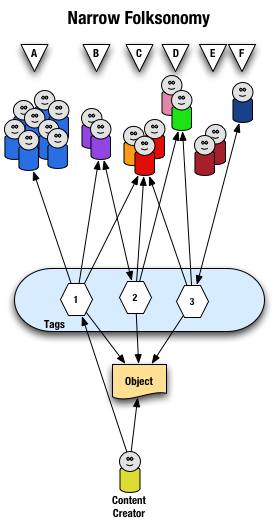
From a high level we see a person creates the object and applies a tag ("1") that represents what they call the object or believe describes the object. There are fewer tags provided than in a broad folksonomy and there is only one of each tag applied to the object. The consumers of the object also can apply tags that help them find the object or describe what they believe are the terms used to describe this object.
A closer look at the interaction between people and the object and tags in a narrow folksonomy shows us that group "A" uses tag "1" to find and come back to the object (did the creator do this on purpose? or did she just tag it with what was helpful to her). We see group "B" also using tag "1" to find the object, but they have tagged the object with tag "2" to also use as a means to find the object. Group "C" uses tag "1","2", and "3" to find the object and we also note this group did not apply any of its own tags to the object as so is only a consumer of the existing folksonomy. We see group "D" uses tags "2" and "3" to find the objects and it too does not add any tags. Group "E" is not able to find the object by using tags as the vocabulary it is using does not match any of the tags currently provided. Lastly, group "F" has their own tag for the object that they alone use to get back to the object. Group "F" did not find the object through existing tags, but may have found the object through other means, like a friend e-mailed them a link or the object was included in a group they subscribe to in their feed aggregator.
We see that the richness of the broad folksonomy is not quite there in a narrow folksonomy, but the folksonomy does add quite a bit of value. The value, as in the case of Flickr, is in text tags being applied to objects that were not findable using search or other text related tools that comprise much of how we find things on the internet today. The narrow folksonomy does provide various audiences the means to add tags in their own vocabulary that will help them and those like them to find the objects at a later time. We are much better off with folksonomies than we were with out them, even if it is a narrow folksonomy being used.
Conclusion
We benefit from folksonomies as the both the personal vocabulary and the social aspects help people to find and retain a tether to objects on the web that are an interest to them. Who is doing the tagging is important to understand and how the tags are consumed is an important factor. This also helps us see that not all tagging is a folksonomy, but is just tagging. Tagging in and of its self is a helpful step up from no tagging, but is no where near as beneficial as opening the tagging to all. Folksonomy tagging can provide connections across cultures and disciplines (an knowledge management consultant can find valuable information from an information architect because one object is tagged by both communities using their own differing terms of practice). Folksonomy tagging also makes up for missing terms in a site's own categorization system/taxonomy. This hopefully has made things a little clearer for all in our understanding the types of folksonomies and tagging and the benefits that can be derived.
This entry first appeared at Personal InfoCloud and comments are open for your use there.
The Future of Newspapers
A state of the newspaper industry article in today's Washington Post tries to define what people want from newspapers and what people are doing to get information.
Me? I find that newspapers provide decent to great content. Newspapers are losing readers of their print versions, but most people I know are new reading more than one paper, but online. The solutions I see from my vantage are as follows.
Ads
The articles rarely have ads that relate to the stories, foolishly missing ad revenues. The ads that are available are distracting and make for an extremely poor experience for the reader. News sites should ban the improperly targeted inducements that rely on distracting from reading the article, which is the reason the person is on that web page. The person has an interest in the topic. There are monetary opportunities to be had if the news outlets were smart and advertisers were smart.
How? If I am reading an article on the San Francisco Giants I would follow and may pay a little something for an ad targeted to this interest of mine. I like to buying Giants tickets, paraphernalia, a downloadable video of the week's highlights, etc. If I am reading about an airline strike a link to train tickets would be a smart option. A news article about problems in the Middle East could have links to books by the journalist on the subject, other background books or papers, links to charitable organizations that provide support in the region. The reader has shown an interest, why not offer something that will also be of interest?
We know that advertisers want placement in what they consider prime territory, the highly trafficked areas of the site. Often this is when the non-targeted ads appear. This is an opportunity to have non-targeted ads pay a premium, say five to 20 times that of targeted ads. The non-targeted ads have to follow the same non-disruptive guidelines that targeted ads follow. This is about keeping the readers around, without readers selling ads does not make any sense.
Archives
One area the news site are driving me crazy is access to the archives. The news sites that require payment to view articles in the archives are shooting themselves in the foot with this payment method and amount required to cough up to see an article that may or may not be what the person interested is seeking. The archives have the same opportunity to sell related ads, which in my non-professional view, would seem like they would have more value as the person consuming the information has even more of an interest as they are more than a casual reader. Any payment by the person consuming the information should never be more than the price for the whole print version. The articles cost next to nothing to store and the lower the price the more people will be coming across the associated advertising.
Blogging and personal sites often point to news articles. Many of us choose whom we are going to point to based on our reader's access to that information at any point in the future. We may choose a less well written article, but knowing it will be around with out having to pay extortionist rates to see it is what many of us choose. Yes, we are that smart and we are not as dumb as your advertisers are telling you. We, the personal site writers are driving potential ad revenues to you for free, if you open your articles for consumption.
Loyalty
Loyalty to one paper is dead, particularly when there are many options to choose to get our news from. We can choose any news source anywhere in the world. Why would we choose yours? Easy access, good writing, point of view, segment coverage (special interests - local, niche industries, etc), etc. are what drive our decisions.
I often choose to make my news selections to include sources from outside my region and even outside my country. Why? I like the educated writing style that British sources offer. I like other viewpoints that are not too close to the source to be tainted. I like well researched articles. I like non-pandering viewpoints. This is why I shell out the bucks for the Economist, as it is far better writing than any other news weekly in the U.S. and it pays attention to what is happening around the world, which eventually will have an impact to me personally at some point in the future. I don't have patience for mediocrity in journalism and the standards for many news sources have really slipped over the past few years.
News sources should offer diversity of writing style and opinion of one source will attract attention. The dumbing down of writing in the news has actually driven away many of those that are willing to pay to read the print versions. Under educated readers are not going to pay to read, even if it is dumbed down. Yes, the USA Today succeeded in that, but did you really want those readers at the loss of your loyal revenue streams?
Loyalty also requires making the content available easily across devices. Time and information consumption has changed. We may start reading an article in the print edition (even over somebody's shoulder and want to follow-up with it. We should be able to easily find that article online at our desk or from our mobile device. Integration of access across devices is a need not a nicety and it is not that difficult to provide, if some preparation is done with the systems. Many of us will pull RSS feeds from our favorite news sources and flag things for later consumption, but the news sites have not caught on how to best enable that. We may pull feeds at one location, but may have the time and focus to read them at another location, but we may not have the feeds there. Help those of us that are loyal consume your information in a pan-medium and pan-device world that we live in.
Amazon and A9 Provide Yellow Pages with Photos
Everybody is talking about Amazon's (A9) Yellow Pages today. Amazon has done a decent job bringing photos into their Yellow Pages for city blocks. This is a nice touch, but it is missing some interaction and interconnections between the photos and the addresses, I hope this will come. I really would like to be able to click on a photo and have the Yellow Pages information show up, everything I tried on Clement Street in San Francisco, California did not work that way.
One of the things that really hit me in playing with the tool today at lunch was how the Yellow Pages still suck. I have had problems with the Yellow Pages for..., well ever. I grew up in cross-cultural environments with British and French influences in my day-time care givers growing up. I moved around a fair amount (up and down the West Coast growing up and Europe and the U.S. East Coast). Culture has their own vocabulary (let alone language) for the same items. What I call things, depends on context, but no matter what, the Yellow Pages do not match what I wish to call what I want (or sometimes need).
Today's search I used one of the Amazon search sample, "Optica", which had some nice references. Knowing how I usually approach using the Yellow Pages I search for glasses (as that is what I need to get or need repaired) or contacts. Doing this in a paper Yellow Pages usually returned nothing or pointers to a couple other places. One would thing online Yellow Pages to be different, well they are, they returned nothing related. Glasses returns restaurant supply and automotive window repairs with not one link to eye glasses, nor a reference to "you may be looking for...".
A9 is a great search tool and Amazon.com has great product tools and incredible predictability algorithms, which will be very helpful down the road for the Personal InfoCloud, but the current implementation is still a little rough. I can see where they are heading with this. And I can dream that I would have this available for a mobile device at some point in the next two or three years.
Once very nice piece that was integrated was reviews and ratings of Yellow Pages entries. This is great for the future, once they get filled out. It will also be great once it is available from mobile device (open API so we can start building a useful tool now?). But, it brings my scenario of the future to light rather quickly, where I am standing in front of a restaurant looking at over 100 restaurant reviews on my mobile device. There is no way that I can get through all of these reviews. Our supporting full complement of context tools will be needed to get pulled into play to get me a couple or four good reviews that will mean something to me.
This is but a small slice of the Personal InfoCloud, which is much broader and focusses on enabling the person to leverage the information they have and find. Pairing these two and enabling easy access to that information when it is needed.
Information Waste is Rampant
Fast Company published costs facing business. The top four relate to poor design and information use: Poor knowledge harnessing ($1.4 Trillion); Digital publishing inefficiencies ($750 billion); Data quality problems ($600 billion); and Paper-based trade processes ($400 billion). That is 3.15 Trillion U.S. dollars down the tubes with no benefit.
The solutions are not that difficult, but everybody seems happy to use the rear view mirror to view the future.
Christina stated, "What me worry" about design and business. The whole CIO is a sham as the CIO is a technology driven person, which is tangentially related to information and technology still hinders information flow if not planned for properly (more on this is coming in the near future here on this site). There needs to be a chief level position that cares about the information, the people using it, and the people who create the information. To Christina's post I responded with the following on her site (posted here so I can better keep track of it):
It seems like the 80s all over again. The focus on design in the to late 80s, mostly with unified branding and creative practices formally brought in-house. There was a lot of push around design, mostly labelled branding (nearly the exact same discussions, but slightly different terms). Much of this was around the brandhouses like Landor. The business community embraced the results and tried to incorporate the creative culture as part of their own.
What happened? The innovators were bought by large advertising or public relation firms and the firms changed their industry term to communication companies. Companies created corporate communication divisions (comprised of adversising, PR, branding, and other creative endevors) and had high level management visability.
By the early 90s the corporate environment had largely subsumed the communication into marketing and business schools that has embraced the creative mindset followed suit. Today marketing is often what trumps design and there is no creative in marketing. The creative departments by the late 90s had been gutted by the web craze. This left business types with little creative craft understanding as those driving what was once good.
It is not suprising that currently named "design" is taking off, as what was good about the creative was gutted and most companies lack central design plans. There is tremendous waste in cross medium design, as few sites are built with an understanding of the digital medium, let alone cross platform design or true cross media design. Part of the problem is far too few designers actually understand cross-platform and/or cross-media design. There is millions wasted in bandwidth on poor web design that is using best practices from the late 90s not those from today. There is no integration of mobile, with a few exceptions in the travel industry. There is still heavy focus on print, but very little smart integration of design in the digital medium. This even applies to AIGA, which is a great offender of applying print design techniques on the web. How can we expect business design to get better if one of the pillars of the design profession has not seemed to catch on?
There are large problems today and we need to break some of our solutions were have been trying to get to solutions that work. Not only do today's solutions not work today, they will not work tomorrow as they are only stop gaps. Cross-platform, cross-device, and cross-medium design solutions are needed, but technology is not here to deliver and few that I have run across in the design world are ready for that change as they have not made the change to today's world.
Today's designer focusses on getting the information in front of the user and stops there. They do not consider how this person or machine may reuse the information. There is so much yet to improve and yet the world is progressing much faster than people can or want to change to keep up. There are designers and developers who will not build for mobile (it is not that hard to do) because they do not see them in the user logs. They fail to see the correlation that their sites suck for mobile and mobile users may test once and go somewhere else for their information. The people that are seeing mobile users in their logs are the ones that have figured out how to design and develop for them properly (most have found that it is relatively inexpensive to do this). This is not rocket science, it is using something other than the rear view mirror to design for now and the future.
Flickr and the Future of the Internet
Peter's post on Flickr Wondering triggers some thoughts that have been gelling for a while, not only about what is good about Flickr, but what is missing on the internet as we try to move forward to mobile use, building for the Personal InfoCloud (allowing the user to better keep information the like attracted to them and find related information), and embracing Ubicomp. What follows is my response to Peter's posting, which I posted here so I could keep better track of it. E-mail feedback is welcome. Enjoy...
You seemed to have hit on the right blend of ideas to bring together. It is Lane's picture component and it is Nadav's integration of play. Flickr is a wonderfully written interactive tool that adds to photo managing and photo sharing in ways that are very easy and seemingly intuitive. The navigations is wonderful (although there are a few tweak that could put it over the top) and the integration of presentational elements (HTML and Flash) is probably the best on the web as they really seem to be the first to understand how to use which tools for what each does best. This leads to an interface that seems quick and responsive and works wonderfully in the hands of many. It does not function perfectly across platforms, yet, but using the open API it is completely possible that it can and will be done in short order. Imagine pulling your favorites or your own gallery onto your mobile device to show to others or just entertain yourself.
Flickr not only has done this phenomenally well, but may have tipped the scales in a couple of areas that are important for the web to move forward. One area is an easy tool to extract a person's vocabulary for what they call things. The other is a social network that makes sense.
First, the easy tool for people to add metadata in their own vocabulary for objects. One of the hinderances of digital environments is the lack of tools to find objects that do not contain words the people seeking them need to make the connection to that object they are desiring. Photos, movies, and audio files have no or limited inherent properties for text searching nor associated metadata. Flickr provides a tool that does this easily, but more importantly shows the importance of the addition of metadata as part of the benefit of the product, which seems to provide incentive to add metadata. Flickr is not the first to go down this path, but it does it in a manner that is light years ahead of nearly all that came before it. The only tools that have come close is HTML and Hyperlinks pointing to these objects, which is not as easy nor intuitive for normal folks as is Flickr. The web moving forward needs to leverage metadata tools that add text addressable means of finding objects.
Second, is the social network. This is a secondary draw to Flickr for many, but it is one that really seems to keep people coming back. It has a high level of attraction for people. Part of this is Flickr actually has a stated reason for being (web-based photo sharing and photo organizing tool), which few of the other social network tools really have (other than Amazon's shared Wish Lists and Linkedin). Flickr has modern life need solved with the ability to store, manage, access, and selectively share ones digital assets (there are many life needs and very few products aim to provide a solution for these life needs or aims to provide such ease of use). The social network component is extremely valuable. I am not sure that Flickr is the best, nor are they the first, but they have made it an easy added value.
Why is social network important? Helping to reduct the coming stench of information that is resultant of the over abundance of information in our digital flow. Sifting through the voluminous seas of bytes needs tools that provide some sorting using predictive methods. Amazon's ratings and that matching to other's similar patterns as well as those we claim as our friends, family, mentors, etc. will be very important in helping tools predict which information gets our initial attention.
As physical space gets annotated with digital layers we will need some means of quickly sorting through the pile of bytes at the location to get a handful that we can skim through. What better tool than one that leverages our social networks. These networks much get much better than they are currently, possibly using broader categories or tags for our personal relationships as well as means of better ranking extended relationships of others as with some people we consider friends we do not have to go far in their group of friends before we run into those who we really do not want to consider relevant in our life structures.
Flickr is showing itself to be a popular tool that has the right elements in place and the right elements done well (or at least well enough) to begin to show the way through the next steps of the web. Flickr is well designed on many levels and hopefully will not only reap the rewards, but also provide inspiration to guide more web-based tools to start getting things right.
Web 2.0: Source, Container, Presentation
At Web 2.0 Jeff Bezos, of Amazon stated, "Web 2.0 is different. It's about AWS (Amazon Web Services). It's not on the web site for users to see. It's about making the internet useful for computers.". This is very appropriate today as it breaks the information model into at least three pieces: source, container, and presentation. Web 1.0 often had these three elements in one place, which really made it difficult to reuse the information, but even use it at times.
The source is the raw information or content from the creator or main distributor. The container is the means of transporting the information or content. The container can be XML, CSV, text, XHTML, etc. The presentation is what is used to make the information or content human consumable. The presentation can be HTML with CSS, Flash, PDF, feed reader, mobile application, desktop application, etc.
The importance of the three components is they most valuable when they stand alone. Many problems and frustrations for people trying to get information and reuse it off the web has been there has not been a separation of the components. Take most Flash files, which tie the container and the presentation in one object that is proprietary and can be extremely difficult to extract the information for reuse. The same also applies to PDF files as they too are less than optimal for sharing information for anything other than reading, if the PDF can be read on the device. As mobile use of the internet increases the separation is much more valuable. The separation has always been the smart thing to do.
Today Google launched a beta of their Google SMS for mobile devices. The service takes advantage of the Google web services (source) and allows mobile users to send a text message with a query (asking "pizza" and providing the zip code) and Google responds with a text message with information (local pizzerias with their address and phone numbers). The other day Tantek demonstrated Semantic XHTML as an API, which provides openly accessible information that is aggregated and reused with a new presentation layer, Flash.
More will follow on this topic at some point in the not too distant future, once I get sleep.